Kontur.Accounting is a web service for small businesses!
Quick establishment of primary accounts, automatic tax calculation, online reporting, electronic document management, free updates and technical support.
Try it
In accounting and tax accounting, income and expenses can be recognized in two ways.
The first one is the accrual method. It is associated with the period of actual conduct of a business transaction. The corresponding income or expense must be taken into account on the date of its occurrence according to documents or on the date of transfer of raw materials or provision of services, that is, at the moment when the income or expense was accrued.
The second option is the cash method. When using it, income or expenses should be recognized in the period when the payment occurred, that is, when money arrived or left the cash register or current account, or when the organization received or transferred other property.
In practice, most often companies keep records using the first method, following the instructions of accounting standards and the Tax Code. It is believed that the recognition of income and expenses upon shipment most accurately reflects the results of the business. However, sometimes businesses may, or are even required to, account for expenses upon payment.
The main advantage of the cash method is the reduction of cash gaps: the situation is eliminated when a company must pay tax, but the funds have not yet been received.
Who can keep tax records of income and expenses using the cash method?
Most often, payers of the simplified tax system switch to the cash method. Such companies have no choice: they cannot keep records of receipts and shipping costs. Some organizations on OSNO also have the right to recognize income and expenses upon payment when calculating income tax. The main condition is that the average revenue excluding VAT for the previous four quarters in each of them should not exceed one million rubles.
Who cannot use the cash method even if the revenue limit is observed (Article 273 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- banks;
- credit consumer cooperatives;
- microfinance organizations;
- companies that are controlling persons of the CFC;
- companies operating in the production of hydrocarbons in a new offshore field.
Another restriction for the listed organizations is the prohibition on concluding property trust management agreements, simple or investment partnership agreements.
Keep records, pay salaries, taxes and contributions, report via the Internet to Kontur.Accounting. The web service itself will calculate the amounts, select transactions, and generate reports. Get free access for 14 days
Differences between the cash method and the accrual method
The difference between the two methods is the period in which income and expenses are recorded.
Income is recognized:
– with the accrual method – in the reporting (tax) period in which they occurred, regardless of the actual receipt of funds and other property ( clause 1 of Article 271 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation );
– with the cash method – on the date of receipt of funds to bank accounts and (or) to the cash desk, receipt of other property, repayment of debt to the taxpayer in another way ( clause 2 of Article 273 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation ).
| Operations | Revenue recognition period | |
| With cash method | With the accrual method | |
| Goods were shipped in the third quarter. Payment received in Q4 | IV quarter | III quarter |
| The advance payment was received in the third quarter. Goods shipped in Q4 | III quarter | IV quarter |
Expenses are recognized:
– with the accrual method – in the reporting (tax) period to which they relate, regardless of the time of actual payment of funds and (or) other form of payment (clause 1 of Article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation );
– with the cash method – after actual payment ( clause 3 of Article 273 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation ), taking into account some features.
When can you use the cash method in accounting?
If we talk about accounting, the legislation specifies a number of organizations that can conduct it in a simplified way. Only such enterprises are allowed to take into account income and expenses at the time of payment. These include small businesses, non-profit organizations and companies with the status of participants in the Skolkovo project. There are some exceptions:
- companies whose reporting is subject to mandatory audit;
- cooperatives (housing, housing construction, credit);
- public sector companies;
- microfinance organizations, etc.
The method of recognizing income and expenses must be fixed in the accounting policy. If a company can use the payment accounting method in both accounting and tax, this will significantly simplify the document flow in the company.
Results
The cash method of recognizing income and expenses in tax accounting under OSNO can be used only if the average amount of income for the last 4 quarters does not exceed 4 million rubles.
If you decide to use the cash method, recognize income on the date of their receipt in the current account or cash register of the enterprise, and expenses - after actual payment. If during the year the right to use the cash method is lost, the tax base will have to be recalculated from the beginning of the year. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
When can you switch to the cash method?
The company can switch to accounting for income and expenses upon payment, subject to the revenue limit, starting from January 1 of the next tax period. A newly registered company has the right to immediately apply this method of accounting. This is advisable if small revenues are expected at first.
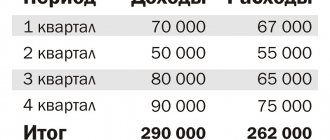
Example. in the OSNO mode, plans to switch to the cash method of accounting from January 1, 2022. Its revenue excluding VAT in each quarter of 2022 was:
1st quarter 2022 - 0.55 million rubles; 2nd quarter 2022 - 1.37 million rubles; 3rd quarter 2022 - 1.21 million rubles; 4th quarter 2022 - 0.62 million rubles.
The average revenue in our case was 0.94 million rubles. This means that Yantar LLC can recognize income and expenses as they are paid.
Loss of the right to work on a cash basis
If certain circumstances arise, including non-compliance with the statutory requirements for the right to use the cash method, the enterprise, regardless of its desire, will have to waive the right to use it. In this case, it is obliged to switch to the accrual method, and this will not have to be done immediately, but from the beginning of the new calendar tax period. The right to use the cash method is limited:
- if the enterprise has entered into a simple partnership agreement or a property trust management agreement;
- if the amount of income from transactions and operations carried out by the enterprise is higher than the legal limit.
The facts presented in this material indicate that the use of the method of cash control over income and expenses, like any other method of tax accounting in commercial companies, has its own nuances, features and subtleties.
Before making a decision on the final transition to it, the company management or individual entrepreneur needs to make sure that it maximally corresponds to the company’s development plans for the near future.
Accounting for income using the cash method
The company has the right to recognize income when payment is received in cash at the cash desk or to the current account. When calculating using an exchange, the date of receipt of income is the day the asset arrives at the organization.
One of the features of post-payment accounting is the recognition of the advance received as income. What to do in a situation where the advance payment needs to be returned? - for example, when terminating a contract with a counterparty and refusing to supply goods or services from our company. In this case, the Tax Code allows these receipts to be deducted from total income.
What settings need to be made in 1C to account for direct and indirect costs
The concepts of direct and indirect expenses in accounting and tax accounting are different.
In accounting, expenses are divided into direct and indirect, depending on the methods of inclusion in the cost of certain types of products. Direct costs are understood as those costs that are associated with the production of certain types of products and that can be directly and directly included in their cost. By indirect we mean costs associated with the production of several types of products, included in their cost using special methods (clause 20 of the “Basic provisions for planning, accounting and calculating the cost of products at industrial enterprises”, approved by the State Planning Committee of the USSR, the State Committee for Prices of the USSR, the Ministry of Finance of the USSR , Central Statistical Office of the USSR 07/20/1970).
The procedure for accounting for costs of producing products, selling goods, performing work and providing services in the context of elements and items, calculating the cost of products (work, services) is established by industry regulations and guidelines for accounting (clause 10 of PBU 10/99).
Direct expenses are recorded in accounts 20 “Main production”, 23 “Auxiliary production”, 29 “Service production and facilities”. Indirect expenses are accounted for in accounts 25 “General production expenses” and 26 “General economic expenses” (Chart of accounts for accounting of financial and economic activities of organizations, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n).
For profit tax purposes, direct expenses may include costs directly related to the production of products, performance of work, provision of services (material costs, personnel costs, insurance premiums, depreciation of fixed assets). The organization has the right to determine the list of direct costs associated with the production of products (performance of work, provision of services). Indirect expenses include expenses incurred in the reporting (tax) period and not classified as direct or non-operating expenses (clause 1 of Article 318 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Direct expenses can be included in the expenses of the current reporting (tax) period only in the amount attributable to the sold products, works, services in the cost of which they are taken into account. And indirect expenses are included in full in the expenses of the period in which they are incurred (clause 2 of article 318 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The procedure for classifying expenses as direct or indirect must be economically justified and determined by the specifics of the technological process, and costs can be classified as indirect only if there is no real possibility of classifying them as direct (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 5, 2018 No. 03-03-06/ 1/ 63428).
The specifics of determining expenses for trade operations are determined by Article 320 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. For trading operations, direct costs include:
- the cost of purchasing goods sold in a given reporting (tax) period;
- the amount of costs for the delivery of purchased goods (transportation costs), if these costs are not included in the purchase price of the specified goods.
All other expenses of trading organizations incurred in the current month, with the exception of non-operating expenses, are recognized as indirect expenses and reduce the income from sales of the current month.
Now about the settings of “1C: Accounting 8”. To reflect production operations, the corresponding functionality must be enabled in the program (section Main - Functionality). On the Production tab, set the flag of the same name.
Methods for distributing indirect costs to include them in the cost of products (works, services) are indicated in the accounting policy settings (section Main - Accounting Policy).
The list of direct expenses for profit tax purposes is indicated in the register Methods for determining direct production expenses in NU. This register is available via the link List of direct expenses from the Income Tax form (section Main - Taxes and reports - Income Tax).
Let's take a closer look at the accounting policy settings (Fig. 3).
Rice. 3. Accounting policies
Please note that some of these settings affect the treatment of direct and indirect expenses in tax accounting.
If an enterprise produces products and/or performs work (provides services) to customers, then it is necessary to enable the flags Production of products and/or Performance of work, provision of services to customers. If at least one of the specified flags is set, the following become available in the Accounting policy form:
- block of settings for accounting general expenses;
- link Methods for allocating indirect costs
; - block of settings for calculating production costs.
In the general expenses accounting settings block there is a General expenses included switch, which can be set to one of the positions:
- In cost of sales (direct ct-costing
). All expenses recorded on account 26 will be written off to the financial result (to account 90.08 “Management expenses”) in the period of their implementation. In tax accounting, these expenses will also be indirect (regardless of the rules established for them in the register Methods for determining direct production costs in NU); - In the cost of products, works, services. All expenses recorded on account 26 will be written off to direct expenses (for example, to account 20.01) in accordance with the procedure specified in the register Methods for distributing general production and general business expenses.
The link Methods for distributing indirect expenses takes you to the register form Methods for distributing general production and general business expenses. The register is intended to store rules for the distribution of general production and general business expenses accounted for in accounts 25 and 26. The Distribution Base field is required, where you can select one of the values:
- Issue volume;
- Planned production cost;
- Salary;
- Material costs;
- Revenue;
- Direct costs;
- Individual items of direct costs;
- Not distributed.
General and general production expenses will be distributed in proportion to the indicator specified in the Allocation Base (for example, the volume of products produced in the current month and services provided, expressed in quantitative terms, etc.).
For general production and general business expenses, you can set the distribution method with detailing down to the department and cost item. This may be necessary when different types of expenses require different distribution methods.
If it is necessary to establish a single distribution method for all general and general production expenses, then when setting the distribution method, you do not need to specify the cost account, division and cost item. You can also set a general distribution method for all expenses accounted for in one account or in one department.
When establishing the distribution method, the register indicates the date from which the distribution method is applied. If it is necessary to change the method of distribution of expenses, a new entry is entered into the information register, which indicates the new method of distribution and the date from which the new method should be applied.
As for trading organizations, no special settings in the Accounting Policy will be required to account for direct expenses.
In accounting and tax accounting, the amount of transportation costs for purchased goods can be included:
- in the cost of goods (for example, using the document Receipt of additional expenses);
- as part of the company’s sales expenses - to account 44.01 “Distribution costs in organizations engaged in trading activities” (for example, using the document Receipt ( act, invoice)
with the type of Service). In order for transportation expenses to be calculated and written off automatically, when registering the receipt of services from a transport company, you must select the value of the expense type as Transportation expenses.
When closing a month using the regulatory operation Closing account 44 “Distribution costs”, sales expenses accounted for on account 44 are written off to account 90.07.1 “Sales expenses for activities with the main tax system” as follows:
- amounts of transportation costs - only in relation to goods sold;
- all other expenses are in full.
| 1C:ITS For more information about closing cost accounts using examples, including accounting for transportation expenses, see the section “Instructions for accounting in 1C programs.” |
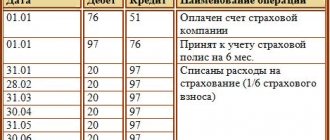
Accounting for expenses using the cash method
The fact of payment is a key event in the cash method. Payment within the framework of recognition of expenses means the termination of a counter-obligation to the seller. The outflow of funds must necessarily be associated with goods, works or services purchased by the company.
When recognizing certain types of expenses, there are additional conditions. For example, for companies on OSNO, the costs of materials and raw materials can be taken into account only as they are sent to production. Depreciation can be taken into account only if the depreciable property is paid for and used in production. For simplified organizations, there is a restriction on accounting for expenses on goods for resale: such expenses are written off as products are sold.
When can an advance paid by a company to a counterparty be taken into account in expenses? Even if the company operates on a cash basis, such a payment cannot be recognized as an expense. Thus, in practice, prepayments to suppliers are recorded at the time of shipment of goods or provision of services/work.
Simplified accounting forms and forms, relevant in 2020
Bookkeeping on the simplified tax system from scratch usually begins with the questions: what accounting documents should an LLC have under the simplified tax system, what forms and forms of documents to use. Federal Law No. 402-FZ has granted broad powers to economic entities in this area, which the Ministry of Finance regularly confirms. For example, instead of a consignment note, it is convenient to use a universal transfer document (Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 21, 2013 No. ММВ-20-3 / [email protected] ). This is what the UPD form, a universal transfer document, looks like:
Basic rules for primary and accounting and tax accounting registers:
- Only events that took place are recorded; the law specifically stipulates liability for records of imaginary transactions.
- All forms are approved in the accounting policy of the organization.
- The documents for which the Federal Tax Service has developed an electronic format have an established structure, but differences in appearance are allowed and have an expanded set of indicators.
- Some primary documents are unified (cash, bank). In addition, accounting, for example, in a travel agency or concert box office in a simplified manner, encounters ticket forms, in laboratories or research centers - with centralized forms of reports and protocols, etc. There are no unified registers.
What happens if the organization violates the terms
When accounting using the cash method, the company must constantly monitor compliance with the income limit. If the limit value has been exceeded for the last four quarters, you need to switch to the shipment accounting method in the current tax period. The same should be done when concluding a trust management agreement or creating a simple or investment partnership.
When returning to the accrual method, either an overpayment of income tax or an arrear arises. You will have to recalculate the tax amount and submit an updated tax return. In case of arrears, the resulting obligations to the budget must be repaid. If these requirements are not met, the company faces fines from the tax authorities.
Account for income and expenses using the cash method in the cloud service Kontur.Accounting. Easily keep records, calculate salaries, automatically generate reports and send them online. The service will remind you of important tasks and dates, updates automatically, and is accessible from anywhere there is Internet access. Test the system's capabilities for free for 14 days.
Try for free
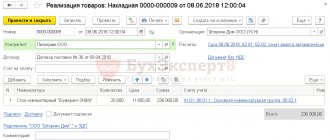
Example of transactions when using the accrual method
In March 2022, Alpha and Omega LLC shipped a batch of flour worth RUB 590,000 to Beta LLC. (including VAT - 90,000 rubles). Beta LLC transferred funds in April. Alpha and Omega LLC uses the accrual method (according to accounting policy).
The following entries are made in the accounting of Alpha and Omega LLC in March:
D62 K90 subaccount “Revenue” – 590,000 rubles. (proceeds from flour)
D90 sub-account “VAT” K68 sub-account “Calculations for VAT” – 90,000 rubles. (VAT is charged on sales).
And the income tax return for the first quarter of 2022 of Alpha and Omega LLC reflects income from the sale of flour in the amount of 500,000 rubles. (590000 – 90000).