The concept of targeted financing
Targeted financing is the allocation of funds for the implementation of strictly defined goals with the ability to control expenses. It could be:
- conducting scientific research;
- capital construction;
- organization of events;
- development of a new line of activity, etc.
According to the sources of funds received, financing is distinguished:
at the expense of the budget (state):
- subsidies - for example, to compensate for housing and communal services costs;
- transfers – for the construction of capital construction projects;
- grants – for carrying out research work.
at the expense of non-governmental organizations:
- scholarships;
- grants;
- investments.
If the financing conditions are met, the funds received become their own, otherwise they will have to be returned, “getting into” accounts payable.
Targeted financing of an organization in 1C Enterprise Accounting
Content:
1. Using accounting account 86
2. Working with a standard operation
3. Movement of targeted financing funds
4. Receipt of equipment
Accounting for the movement of funds issued for a specific purpose for carrying out events, programs or projects is a complex process of economic activity in non-profit organizations.
When an organization receives targeted funds, it must use them within the framework of an agreement with the investor who allocated these funds. For example, if an organization is allocated funds to build a playground, it cannot spend them on building a parking lot. The Civil Code of the Russian Federation does not contain the concept of “agreement on targeted financing”. Therefore, the receipt of funds from non-state targeted financing of an organization can be formalized by an agreement drawn up in any form, in accordance with clauses 2 and 4 of Art. 421 Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Using accounting account 86
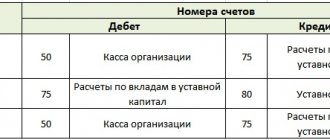
According to the chart of accounts in 1C: Enterprise Accounting, edition 3.0, accounting for the movement of financing assets is carried out using accounting account 86 “Targeted financing”. Account 86, unlike settlement accounts with counterparties, is only passive - it cannot have a debit balance. Transactions of receipt or reflection of target funds increase Credit 86, and transactions that use target funds increase Debit 86.
Also, accounting account 86 does not correspond with the settlement accounts of counterparties: 60 – Settlements with suppliers and 62 – Settlements with customers. Account 86 corresponds with only one of the counterparty's current accounts, namely: account 76 – Settlements with various debtors and creditors.
To reflect business transactions with account 76, it is necessary to use accounting transactions, since the standard delivery of the 1C: Enterprise Accounting 3.0 configuration does not provide documents for reflecting transactions with accounts 86 and 76. If such accounting transactions will be repeated, then it is more convenient to create standard transactions. To do this, in the “Operations” menu, open “Typical operations”.
Working with a typical operation
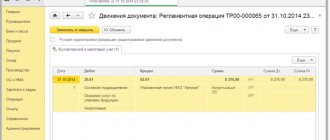
Let's create a new standard operation. For example, you will often need to use the transaction with posting Dt 76.05 Kt 86.02. To do this, we indicate these accounts in the tabular part of accounting and tax accounting, respectively. We indicate the content of a typical operation and write it down.
The next time you need to reflect the receipt of other target funds, you can open the transactions entered manually and, when creating a new one, select the created standard transaction.
In the operation that opens, you must click the “Fill” button, after which the transactions will be filled out in the “Accounting and Tax Accounting” tabular section. Next, all that remains is to fill out the necessary analytics. Also, if, in addition to accounts, analytics are regularly repeated, for example, “Movements of target funds,” then it can also be specified when creating a standard operation.
Movement of targeted financing funds
To reflect movements of funds for targeted financing in 1C, four types of documents are most often used: cash orders, payments, invoices and accounting transactions entered manually. Let's look at each of them using the example of the 1C software product: Enterprise Accounting, edition 3.0.
For example, you need to register the receipt of other funds for the purpose of construction in the amount of 100 thousand rubles to the cash desk of the organization Abramov G.S. IP. To do this, in the “Bank and Cash Office” menu, open “Cash Documents”.
Let’s create a “Cash receipt” document. You need to indicate the type of transaction “Other receipt”, credit account 86, the amount of receipt, organization and other necessary analytics.
As a result of the document, the receipt of targeted financing in the amount of 100 thousand rubles to the cash desk will be reflected (Dt 50.01Kt 86.02).
Let's assume another situation, when money for construction should not go to the cash desk, but to the bank account of the organization Abramov G.S. IP. To do this, in the “Bank and Cash Desk” menu, you need to open “Bank Statements” and create a “Receipt to Current Account” document.
In the created document, you need to indicate the type of transaction “Other receipt”, credit account 86, the amount of receipt, organization and other necessary analytics.
As a result of the document, the receipt of funds for construction will be reflected in the current account of the organization Abramov G.S. IP (Dt 51 Kt 86.02). By analogy, you can register the receipt of funds for financing purposes to a foreign currency account (Dt 52 Kt 86) and a special bank account (Dt 55 Kt 86).
Receipt of equipment
Next, we will consider the receipt of “Machine” equipment, which is necessary for construction - an event in accordance with its intended purpose. To reflect this business transaction, you need to create a document “Receipt of goods: Invoice”. It can be found in the menu “Purchases – Receipts (acts, invoices)”.
In the created document you need to indicate Account for settlements with counterparties 86.02.
You also need to select the “Machine” item with the item type “Equipment for installation” and accounting account 07.
As a result of the document, the “Machine” equipment intended for construction will be capitalized under a targeted financing agreement (Dt 07 Kt 86.02). By analogy, you can register investments in non-current assets received as investments (Dt 08 Kt 86), capitalize materials intended for targeted activities (Dt 10 Kt 86), capitalize animals provided as targeted financing (Dt 11 Kt 86) and etc.
We will also consider the fourth type of document: accounting transactions entered manually. For example, if the organization “Abramov G.S. IP” needs to include 100 thousand rubles for construction under contract 1 dated 01/01/2020 as part of deferred income for the counterparty Ernest Yakovlevich Golovanov under contract 1 dated 01/01/2020, then in 1C: Accounting Enterprise 3.0 reflection of such an operation will look like this:
Specialist
Lyubov Starygina
Postings to reflect target financing on account 86
In general, accounting entries for account 86 in commercial organizations look like this:
- Dt76 – Kt86 – reflects the receipt of targeted funds;
- Dt86 – Kt98 – target money is reflected as prospective income;
- Dt60 – Kt51 – payment has been made to the supplier for materials or goods;
- Dt10 – Kt60 – materials or goods delivered to the receipt;
- Dt20 – Kt10 – materials are written off;
- Dt91 – Kt20 – expense account is closed;
- Dt98 – Kt91 – targeted funds are reflected in the line of other income.
Records of the movement of received amounts depend on the nature of the activity of the economic entity. Thus, non-profit organizations can directly reflect the receipt of materials by posting Dt86 - Kt20 .
Explanations
Targeted financing is the gratuitous receipt of money, which can only be spent according to the program provided by the entity that allocated it. Simply put, the ability to spend the received amounts is limited by certain conditions. When fulfilled, the funds become the property of the enterprise. If the established conditions are not met, the company must return all amounts received. In this case, they will be classified as accounts payable.
What does the balance show and how is account 86 closed?
The credit part of account 86 displays the amount of funds allocated to the company under the terms of targeted financing. Its debit part reflects the unused balance, which will be spent in the future or returned to the investor.
In a standard situation, when the funds received under the contract were spent on the implementation of contractual goals in full, no additional entries are required to close the account. If the funds remain, then the accountant will have to reflect their further movement:
- if the balance can be used by the company at its own discretion, then posting Dt86 - Kt90 (sales) or Dt86 - Kt91 (other income) will be required;
- if the balance must be returned to the “sponsor”, then the posting looks different - Dt86 - Kt51 (non-cash payment), Dt86 - Kt50 (cash payment), Dt86 - Kt52 (payments in foreign currency).
Account 86 in accounting
An important aspect of accounting for these funds is the competent determination of their purpose and purpose in accordance with the agreement.
Sources of financing activities (funds for special purposes) are reflected in credit 86 of the accounting account, and their use itself is reflected in debit:
Subventions are funds from the budget that are provided on the condition of shared financing of targeted expenses to a legal entity (in order to reduce production costs) or to an individual, or to the budget of another level of the RF BS.
Analytical accounting of target funds is carried out according to their purpose and sources of income.
Attention! It is prohibited to use designated funds for other purposes.
Accounting for receipt and write-off of target funds using examples
For a detailed examination of various operations using target revenues, we use illustrative examples of typical situations.
Receiving government subsidies
JSC “Minister” operates in the field of real estate construction. In March 2016, “Minister” took part in a tender to receive government subsidies for their subsequent use for the construction of social housing. The amount of state aid is 3,478,000 rubles.
In April 2016, upon completion of the tender, JSC “Minister” was recognized as the winner, and therefore funds in the amount of 3,478,000 rubles were credited to the organization’s current account. In addition, the Minister received construction materials in the form of state aid, the cost of which amounted to 1,714,200 rubles.
The received government subventions were taken into account by the “Minister” in the following way:
| Debit | Credit | Operation description | Sum | A document base |
| 76 Targeted financing funds | 86 | The amount of funds accrued as government subventions is reflected (RUB 3,478,000 + RUB 1,714,200) | 5,192,200 rub. | Targeted financing agreement |
| 51 | 76 Targeted financing funds | The funds received by the “Minister” as a state target program are taken into account | RUB 3,478,000 | Bank statement |
| 10 | 76 Targeted financing funds | Materials received by the “Minister” for use in the construction of social housing were taken into account | 1,714,200 rub.) | Bank statement |
Reimbursement by the state for lost income
As part of the state program, JSC “Canteen No. 1” provides social food distributions to preferential categories of the population. The cost of rations issued to Canteen No. 1 in November 2015 is 412,850 rubles. This amount is fully compensated from the state budget.
The accountant of Canteen No. 1 made the following entries in the accounting records:
| Debit | Credit | Operation description | Sum | A document base |
| 51 | 76 Targeted financing funds | Funds have been transferred from the budget within the framework of the state program for assistance to social categories of citizens. | RUR 412,850 | Bank statement |
| 76 Targeted financing funds | 90.1 | Reflects compensation for revenue lost to Canteen No. 1 in connection with the issuance of food rations | RUR 412,850 | Agreement |
Investment of targeted proceeds in non-current assets
Progress JSC is engaged in the production of medical equipment. An agreement was concluded between JSC Progress and the charitable organization Mecenat, according to which:
- “Progress” receives funds from “Maecenas” in the amount of 1,953,500 rubles;
- the funds should be used to purchase an improved conveyor line, which will increase the production of medical equipment.
In September 2015, funds were received from Maecenas, the conveyor line was purchased and put into operation:
- cost of the conveyor line - 1,953,500 rubles;
- useful life – 12 years;
- the amount of monthly depreciation is 12,522 rubles. (RUB 1,953,500 / 13 years / 12 months).
The receipt of funds from “Maecenas”, the acquisition and commissioning of the conveyor line were recorded in the accounting records of “Progress” with the following entries:
| Debit | Credit | Operation description | Sum | A document base |
| 76 Targeted financing funds | 86 | The amount of accrued funds is reflected as received under an agreement with BO “Mecenat” | 1,953,500 rub. | Agreement |
| 51 | 76 Targeted financing funds | Targeted funds received from the charity “Mecenat” are taken into account | 1,953,500 rub. | Bank statement |
| 08 | 60 | The receipt of the purchased conveyor is reflected | 1,953,500 rub. | Packing list |
| 01 | 08 | The operation to put the conveyor into operation was carried out | 1,953,500 rub. | OS commissioning certificate |
| 86 | 98 | The intended use of funds received from the charitable organization “Mecenat” is reflected | 1,953,500 rub. | Agreement, Consignment note, OS commissioning certificate |
| 20 | 02 | The amount of monthly accrued depreciation on the conveyor is taken into account | RUB 12,522 | Depreciation statement |
| 98 | 91.1 | Other income is taken into account from the amount of deferred income (in the amount of accrued depreciation) | RUB 12,522 | Depreciation statement |
Use of targeted funds for current needs
JSC “Consul”, under a targeted financing agreement, transferred funds to LLC “Zoo” in the amount of 642,300 rubles. Funds have been provided for the repair of animal enclosures. Using the funds received from the Consul, the Zoo purchased the materials necessary to repair the enclosures. The actual repairs were carried out by the Zoo’s own staff.
The following transactions are recorded in the Zoo’s accounting records:
| Debit | Credit | Operation description | Sum | A document base |
| 76 Targeted financing funds | 86 | Reflects the amount of accrued funds on account of receipt under the agreement with JSC “Consul” | 642,300 rub. | Agreement |
| 51 | 76 Targeted financing funds | Targeted funds received from JSC “Consul” are taken into account | 642,300 rub. | Bank statement |
| 10 | 60 | The Zoo warehouse received materials purchased for the repair of animal enclosures | 642,300 rub. | Packing list |
| 86 | 98 | Materials purchased for repairs are accounted for as deferred income | 642,300 rub. | Packing list |
| 20 | 10 | The fact of using materials in the repair of animal enclosures is reflected | 642,300 rub. | Packing list |
| 98 | 91.1 | Other income from the amount of deferred income is taken into account | 642,300 rub. | Agreement, Consignment note |