What the law says
The terms of remuneration for each employee are determined in an employment or civil law contract.
The employer is obliged to make payments established in the agreement in full and within the agreed period. If the earnings were not calculated in full or the employee is overpaid, then the employer has the right to recalculate. Moreover, the employer will have to pay the underpaid money in any case. But the overpayment may not be collected. This decision is made by the employer on an individual basis.
The following grounds for recount are established by law:
- counting error;
- remunerations calculated at the end of the year;
- change in working conditions under the contract;
- increasing the minimum wage;
- By the tribunal's decision;
- by decision of the labor dispute commission;
- instructions from GIT inspectors;
- earnings indexation;
- downtime, failure to comply with labor standards or duties;
- unearned advances and vacations.
Each basis for recalculation has its own characteristics. Responsibility is provided for failure to comply with the requirements for recalculating wages for previous months.
How is salary indexation taken into account?
The employer is obliged to index wages annually. Indexation affects the calculation of average earnings, which is determined for vacation pay, sick leave, etc. Average earnings are calculated based on the previous 12 months. Salaries for the previous year are recalculated as follows:
- the salary and payments depending on it, accrued before the indexation, are increased by the indexation factor;
- other payments (in a fixed amount) do not change.
Example 1
Semenov S.S.
upon hiring on October 1, 2017, the salary was set at RUB 30,000. and a bonus for qualifications of 20% of the salary (6,000 rubles). From 02/01/2019, wages were indexed throughout the enterprise. In Semenov S.S. from this moment the salary is 33,000 rubles. and bonus - 6600 rubles. In addition, in October 2018, the employee was paid a bonus in the amount of 10,000 rubles. As of August 1, 2019, the employee goes on vacation. It is necessary to calculate his average earnings (the entire period has been worked out in full). Payments from February to July 2022 are taken into account in the accrual amount:
Changes in wage conditions
The amount and procedure for remuneration are essential terms of the employment agreement. And with any adjustment to the agreements, the employer must not only reflect the changes in the contract. A salary recalculation is also required.
Often, changes in earnings are made in connection with an increase in the level of wages in the company, an increase in the minimum wage, or a complete change in the wage system in the organization. In all cases, employees must be notified of upcoming changes and salary recalculation in the prescribed manner.
Wage cuts are carried out much less frequently. But circumstances can turn out this way. If wage conditions worsen, employees must be notified of changes in remuneration at least two calendar months in advance. The same period is provided for reduction. For example, when an employee is transferred from full time to 0.75 or part time.
Let us briefly remind you how to formalize the recalculation of wages. Firstly, an order or other order from the manager is required to change the terms of remuneration. Then the new rules and calculation procedure are fixed in the employment contract with the employee. For example, an additional agreement is concluded.
Based on correctly completed personnel documentation, the accountant will recalculate the wages of an employee whose payment conditions have changed.
Errors in salary calculations
No one is immune from mistakes. A payroll accountant is no exception. Therefore, errors in calculating employee earnings are common. How to correct the identified defect depends on the result of the error.
For example, it may be necessary to recalculate wages if an underpayment is detected. In other words, the employee was actually paid less than he earned. The employer must correct the mistake and transfer the money. Moreover, no additional consent is required from the subordinate to recalculate upward. The basis for additional payment is the order of the manager.
If an overpayment is detected, the situation changes dramatically. An employer can forgive overpayment to a subordinate. For example, as a reward for good work or out of the kindness of your heart. But it also has the right to retain the surplus by issuing an order.
A number of requirements must be met:
- The retention period cannot exceed one calendar month from the date of the error.
- The employee must submit an application for recalculation of wages or written consent to deduction.
- It is possible to issue a return through the cashier. That is, the subordinate returns the excess in one amount at once.
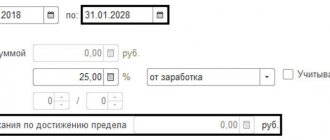
- Partial withdrawals from earnings are possible. For example, in the amount of 25% of the salary, until the overpayment is fully repaid. Determined in the employee’s application for salary recalculation.
- The subordinate has the right to challenge the employer’s demands to withhold the overpayment.
The employee’s consent is drawn up in the form of a document.
IMPORTANT!
Even with the written consent of the subordinate, it is impossible to deduct more from the employee’s salary than is established at the legislative level: the recalculation of wages (Article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation No. 137) cannot exceed the restrictions on the maximum amount of deductions. We will have to postpone part of the research to next month.
A counting error should be considered arithmetic shortcomings in the calculation of wages. They also include software failures when working in specialized accounting programs. But technical errors (for example, errors when entering data into the program, using incorrect data in calculations) made through the fault of the employer are not countable. Salary adjustments are not made due to technical errors.
Additional payroll
Errors in payroll are not uncommon. And it is not always possible to identify the error on your own. In cases where labor inspectors found a mistake, the consequences cannot be avoided. However, the accountant is afraid not so much of the responsibility as of the work that will have to be done in the event of additional payroll.
The employer's financial liability for delayed payment of wages is established by Art. 236 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. If the employer violates the established deadline for payment of wages, the employer is obliged to pay it with interest (monetary compensation) in the amount of not less than one three hundredth of the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation in force at that time from amounts not paid on time for each day of delay (starting from the next day after the established payment period up to and including the day of actual settlement). The amount of monetary compensation paid to an employee may be increased by a collective agreement, local regulation or employment contract. The obligation to pay the specified monetary compensation arises regardless of the employer’s fault.
But, as we said above, the accountant’s work will not end with the payment of compensation. The main thing is ahead. After all, the error still needs to be corrected in accounting. The question arises: is it necessary to correct reports to the Pension Fund and Social Insurance Fund and clarify personal accounting information?
IMPORTANT IN WORK
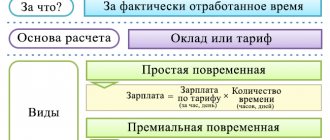
The employee’s salary, a component of which (depending on the remuneration system used by the employer) is the tariff rate, according to Art. 135 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is established by an employment contract in accordance with the current employer’s remuneration system.
Example.
The State Labor Inspectorate conducted an inspection in a company using the simplified tax system with the object “income”. As a result of the audit, errors were discovered in the calculation and payment of wages for 2014 and the first quarter of 2015. As a result of the inspection, the inspector decided to pay additional wages to the company's employees. The financial statements for 2014 have been signed. The error is not significant.
GOOD TO KNOW
The rules for correcting errors and the procedure for disclosing information about errors in accounting and reporting are established by PBU 22/2010 “Correcting errors in accounting and reporting.”
Accounting
In accordance with clause 2 of PBU 22/2010, incorrect reflection (non-reflection) of facts of economic activity in the accounting records or financial statements of an organization is recognized as an error.
In the situation under consideration, the organization incorrectly calculated and paid wages to employees for the reporting period of 2014 and the first quarter of 2015. Identified errors and their consequences are subject to mandatory correction (clause 4 of PBU 22/2010). An error in the reporting year identified before the end of that year is corrected by entries in the relevant accounting accounts in the month of the reporting year in which the error was identified (clause 5 of PBU 22/2010).
Consequently, the underaccrued amount of wages for the first quarter of 2015 is reflected in accounting in the usual manner in the month in which the error was discovered.
| Debit | Credit | Operation |
| 20 (23, 25, 26, 44, etc.) | 70 | Additional wages accrued |
| 20 (23, 25, 26, 44, etc.) | 69 | Additional insurance premiums have been added |
| 70 | 68 | Personal income tax withheld |
| 70 | 51 (50) | Salary transferred |
| 68 | 51 | Personal income tax paid |
| 69 | 51 | Insurance premiums paid |
PBU 22/2010 establishes a different procedure for correcting an error of the previous reporting year, identified after the date of signing the financial statements for this year, depending on whether this error is significant. An error is considered significant if it, individually or in combination with other errors for the same reporting period, can affect the economic decisions of users made on the basis of the financial statements compiled for this reporting period.
The organization determines the materiality of the error independently based on both the size and nature of the relevant item(s) of the financial statements.
Based on the provisions of paragraph 3 of PBU 22/2010, the criteria for the materiality of an error must be specified in the accounting policies of the organization.
An error of the previous reporting year, which is not significant, discovered after the date of signing the financial statements for this year, is corrected by entries in the corresponding accounting accounts in the month of the reporting year in which the error was identified. Profit or loss arising as a result of correcting this error is reflected as part of other income or expenses of the current reporting period (clause 14 of PBU 22/2010).
The procedure for correcting a significant error is established in paragraphs. 7–13 PBU 22/2010.
In this case, for example, small businesses, with the exception of issuers of publicly offered securities, as well as socially oriented non-profit organizations have the right to correct a significant error of the previous reporting year, identified after the approval of the financial statements for this year, in the manner established by clause 14 of PBU 22/ 2010, without retrospective recalculation (paragraph 6, paragraph 9 of PBU 22/2010).
In the situation under consideration, the mistake made is not significant for the organization; accordingly, additional payroll for 2014 is reflected in the following entries:
| Debit | Credit | Operation |
| 91 | 70 | Additional wages accrued |
| 91 | 69 | Additional insurance premiums have been added |
| 70 | 68 | Personal income tax is withheld from wages paid |
POSITION OF THE MINISTRY OF FINANCE
The amount of compensation calculated on the basis of 1/300 of the current refinancing rate (minimum amount) is not subject to personal income tax, regardless of whether the payment of interest is provided for by the collective (employment) agreement or not.
— Letter dated April 18, 2012 No. 03-04-05/9-526.
Don’t forget to also pay compensation for delayed wages. Compensation (interest) for delayed wages is inherently a sanction for violation of obligations. Fines, penalties, penalties for violation of the terms of contracts are accepted for accounting in amounts awarded by the court or recognized by the organization (clause 14.2 of PBU 10/99).
Based on the provisions of clause 12 of PBU 10/99, such expenses of the organization are classified as other and are reflected in the debit of account 91 “Other income and expenses”, the subaccount “Other expenses” and the credit of account 73 “Settlements with personnel for other operations”.
In accounting, monetary compensation in case of violation of the established deadline for salary payment is recognized as other expenses (clause 11 of PBU 10/99). The accrual and payment of compensation is reflected in the following entries:
| Debit | Credit | Description |
| 91, subaccount “Other expenses” | 73 | The amount of interest for delayed payment of wages is included in other expenses |
| 91, subaccount “Other expenses” | 69 (according to subaccounts) | Insurance premiums have been calculated for the amount of compensation |
| 73 | 50 (51) | Compensation paid for delayed wages |
POSITION OF THE MINISTRY OF HEALTH AND SOCIAL DEVELOPMENT
Compensation paid on the basis of Art. 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, is subject to insurance premiums on a general basis, since Art. 9 of Law No. 212-FZ, it is not directly mentioned among non-taxable payments.
— Letter dated March 15, 2011 No. 784-19.
Reporting to the Pension Fund and the Social Insurance Fund
Article 17 of Law No. 212-FZ provides for cases in which the payer of insurance premiums should make changes to previously submitted calculations (according to forms RSV-1 PFR and 4-FSS):
- If it is discovered that information is not reflected or is incompletely reflected, as well as errors leading to an underestimation of the amount of insurance premiums payable, the payer of insurance premiums is obliged to make the necessary changes to the calculation and submit to the body monitoring the payment of insurance premiums an updated calculation of accrued and paid insurance premiums (h 1 Article 17 of Law No. 212-FZ);
- If the payer of insurance premiums detects inaccurate information in the calculation of accrued and paid insurance premiums submitted to the body for monitoring the payment of insurance premiums, as well as errors that do not lead to an underestimation of the amount of insurance premiums payable, the payer of insurance premiums has the right to make the necessary changes in the calculation of accrued and paid insurance premiums and submit to the body monitoring the payment of insurance premiums an updated calculation of accrued and paid insurance premiums. At the same time, an updated calculation of accrued and paid insurance premiums, submitted after the expiration of the established deadline for submitting a calculation of accrued and paid insurance premiums, is not considered submitted in violation of the deadline (Part 2 of Article 17 of Law No. 212-FZ).
ORIGINAL SOURCE
The date of payment and other remuneration is considered the day they are accrued by payers of insurance premiums in favor of the employee.
— Clause 1 of Art. 11 of Law No. 212-FZ.
In letters from the Federal Social Insurance Fund of Russia dated November 17, 2011 No. 14-03-11/08-13985, the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated May 28, 2010 No. 1376-19 explained that the discovery in the current reporting (calculation) period of the need to withhold payments from employees that were excessively accrued them in past reporting (calculation) periods, or, conversely, to accrue additional payments for past reporting (calculation) periods does not reveal an error in calculating the base for calculating insurance premiums, since in each of the specified periods (past and current) the base for calculating insurance premiums was defined as the amount of payments and other remunerations accrued in favor of employees in that period. Therefore, changes to the calculation of accrued and paid insurance premiums for past periods are not required in the situations under consideration.
Thus, there is no need to correct reporting on insurance premiums for 2014 and for the first quarter of 2015 in the situation under consideration.
GOOD TO KNOW
The calculation period for insurance premiums is a calendar year. Reporting periods are the first quarter, half a year, nine months of a calendar year, and a calendar year.
Salary recalculations based on court decisions
One of the grounds on which the employer will have to recalculate wages for the previous year is a court decision or the conclusion of another authorized body. For example, a decision of the state labor inspectorate or the conclusion of a labor dispute commission.
The decision to recalculate earnings can be made either at the initiative of the employee or at the request of the employer. It all depends on the circumstances. For example, if an employer does not pay wages on time and in full, then a subordinate can seek justice through the court.
The employer also has the right to demand the withholding of excessively transferred remuneration through the court. For example, if an employee received an advance, but did not work it out. A similar appeal to the court may be required if the employee took vacation for a year that was not fully worked.
How to draw up an accounting certificate on salary recalculation
There is no unified form that commercial organizations can use. Therefore, you can use form 0504833, intended for government agencies, or draw up a certificate in free form. For example, like our sample.
So, what you need to indicate in the help:
- Name of the organization and its details.
- The name of the document, the date of its preparation and number.
- The essence of the operation, the calculations performed. Here you need to indicate why the employee needs to recalculate the salary, how much needs to be added to the employee or withheld from him. You also need to indicate other subtleties: for example, if part of the salary is delayed, the employer must pay the employee appropriate compensation.
- Position and full name of the employee who compiled the document.
- Signature of the employee responsible for drawing up the certificate. In addition, the certificate must also be signed by the chief accountant. If the document was drawn up by the chief accountant himself, then only his signature is sufficient.
How to recalculate
There is no single procedure for recalculation - all situations are individual. Here are the key rules and recommendations:
- Corrections can be made manually. Or use specialized accounting programs for calculations.
- Make adjustments to calculations only on the basis of administrative documentation.
- If you need to make a deduction from earnings, be sure to obtain the employee’s consent.
- Follow the deadlines for recalculations when errors are identified. It is possible to correct an accounting deficiency in the accrual only within a calendar month.
IMPORTANT!
It is impossible to withhold wages without the written consent of a subordinate, regardless of the types of payments and the reasons for the transfer. An employee can challenge any actions of the employer in court.
Period for recalculation
The amount of earnings is recalculated for the period when the salary was calculated incorrectly. Immediately after discovering an error, the employer must return the underpayment to the employee, if any.
In some cases, it may be necessary to recalculate earnings for the previous year. This is also acceptable, but comes with additional complications. In this situation, it will be necessary to make appropriate adjustments to the tax reporting documentation, if it has been submitted.
If an accountant made a calculation error and calculated a salary in a larger amount, then the result may be arrears in income tax , since the tax base was unfairly reduced. Based on the recalculation according to the provisions of Art. 54, 81 of the Tax Code, the accountant needs to submit an updated declaration. When recalculated for other reasons, it is absent.
As for the need for deductions from wages, this does not reduce the tax base for personal income tax. If the salary itself decreases, then the excessively withheld personal income tax must be returned.
If it increases, personal income tax is withheld and transferred to the budget when recounting payments are made.
Personnel registration
All payment changes must be documented. Including recounts. We will present the paperwork in a summary table.
| Recalculation situation | List of documents |
| Error in calculations | An order from the accounting department to recalculate wages, signed by the manager. Written consent of the employee to deduct from earnings. |
| Court decisions | Conclusion or decision of a judicial body, labor dispute commission or requirement of a State Labor Inspectorate inspector. It is possible to issue an order for the execution of a court decision. |
| Changes in wage conditions | Payment change order. Additional agreement to the employment contract. Regulations on remuneration when changing the SOT. Notifications to employees about changes in pay (if payments are reduced). New staffing (with a reduction in rates). Tariff lists and tariffs. |
| Increase in minimum wage | Order from the manager to increase the minimum wage. Additional agreement to the employment contract. |
Refund due to inaccuracy in calculations
To withhold overpaid wages on this basis, it is important to understand that wages mean remuneration for work, since the above prohibition does not apply to other payments.
Information on how to distinguish payments included in wages from other types of remuneration can be found in the article “What are the types of bonuses and employee benefits? ”
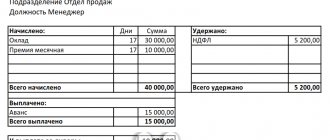
Inaccuracy in calculations is grounds for the return of overpaid wages if the person who calculated it made an error. For example, when adding the amounts of bonus (200 rubles) and salary (10,000 rubles), instead of 200, 2,000 was entered into the calculation (i.e., an extra zero was indicated), etc.
See also “Program crash—counting error or not?”
As a result of a calculation error, the amount of insurance premiums and withheld personal income tax automatically increases. Find out how to correct these indicators if an error is detected in the calculations in ConsultantPlus. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial demo access. It's free.
Deadlines and limitation periods for recalculation
It is not always possible to recalculate employee benefits. It is important to comply with the statute of limitations. Legislators have established the following restrictions:
- in relation to workers, it is allowed to carry out recalculations throughout the entire period of validity of the employment contract;
- if it is necessary to recalculate wages after dismissal, this is allowed only within three months from the date of termination of the employment contract or from the day the employee learned of the underpayment.
If labor rights are violated, the injured party has only three calendar months to go to court. The statute of limitations is calculated from the moment the offense was committed or from the moment the injured party learned of the violation of rights.
IMPORTANT!
Claim periods for recalculation of wages in case of underpayment in labor disputes may be increased, but only for good reasons. For example, the illness of the plaintiff himself, an accident, a natural disaster or illness of close relatives. The circumstances will have to be documented.
Controversial issues and situations of salary recalculation
We will answer the most popular questions about recalculating earnings.
1. Is it possible to recalculate the income of a subordinate for previous periods?
Can. Labor legislation does not limit the timing of recalculation. But if there are any disagreements, disputes will have to be resolved in court.
2. Is recalculation allowed after dismissal?
Yes, it is allowed. The employee has the right to apply for a recalculation within three months from the date of dismissal. Or within three months from the day on which the underpayment became known.
3. How to recalculate the salary of a working pensioner?
According to general rules. There are no exceptions, restrictions or privileges for salary recalculation for working pensioners.
4. What about taxation?
Recalculate taxes and contributions in the billing period in which the error was identified or recalculation was made. When the amount is withheld from a subordinate, personal income tax and insurance premiums are subject to reduction. If you have identified an underpayment, recalculate taxes, fees and contributions upward.
5. The employer refuses to pay the underpayment of wages, what should the employee do?
Follow the algorithm:
- submit a written statement to your employer;
- duplicate the application to the trade union committee of the organization;
- if there is no response or action, contact the labor inspectorate (in person, by mail, via the Internet);
- go to court with a claim for violation of labor rights.
IMPORTANT!
The employer bears administrative responsibility for violation of labor legislation. The amount of penalties depends on the severity of the violation and the statute of limitations for the offense.
Voluntary debt repayment
If the advance payment is returned, there will be no need to make adjustments to insurance premiums, since insurance premiums are not charged from the advance amounts. The same applies to personal income tax, if the employer does not withhold tax from advances paid.
If it is withheld, then the transferred tax will have to be returned to the current account or counted against future payments to the budget, and an updated 2-NDFL certificate will be issued for the employee if the tax period in which the overpayment occurred has expired.
When returning vacation pay, the accountant must reverse the accrual entry and cancel expenses in the form of accrued vacation pay in tax accounting.
There is an overpayment of insurance premiums. For the current period, it is necessary to take into account the adjustments for their accrual, and the overpayment should be adjusted with further payments.
If, in connection with the deletion of accrual of vacation pay, negative values are formed in the personalized accounting in the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation for an employee, the company’s report will not be accepted. Therefore, you will have to adjust not the current period, but the previous period.
An overpayment of personal income tax is formed, withheld from the amount of vacation pay and transferred to the budget. If Certificate 2-NDFL for the corresponding year has been submitted, you need to make an updated certificate - the current date with the old number.
The posting for accrual of personal income tax on vacation pay is reversed. The resulting tax overpayment can be returned to your current account or offset against future payments to the budget.
See examples in the booklet “Practical Encyclopedia of Accountants”
Overpayment of wages