To control the expenditure of funds issued to employees, an advance report is used. It can also be used to report payments for services or purchases of goods in the interests of the company without first receiving money. True, the latter approach is not welcomed by the tax authorities.
Accounting and calculations related to accountable amounts are regulated at the legislative level by the Bank of Russia Directive No. 3210-U, the Chart of Accounts and instructions thereto, the Accounting Law No. 402-FZ, the Regulations approved by Government Decree No. 749 of October 13, 2008, the Labor Code and other acts. Additionally, it is necessary to be guided by clarifications and letters from departments such as the Ministry of Finance or the Federal Tax Service.
The rules for working with accountants within the company are regulated by orders and regulations. For example, regulations on business trips or settlements with accountable persons, a document flow schedule. You can use the standard form - AO-1 or develop it yourself, keeping the main details:
- Name;
- date of compilation;
- Name of the organization;
- Full name and signature of the reporting person;
- data on expenses incurred and supporting documents;
- positions of persons responsible for verification and approval.
Note! The non-standard form is part of the accounting policy or is an appendix to it, like other forms used in business. Accounting programs usually use standard forms.
Money in the morning, chairs in the evening
The principle that was practiced by the hero of the film “12 Chairs” also applies to the expense report. Judging by clause 6.3 of Directive No. 3210-U and clause 10 of the “Regulations...” you first need to give the money to the employee so that he can then account for it. But Article 168 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation talks about reimbursement of travel expenses (which can be considered as compensation without prior issuance of funds). It is recommended that local regulations provide for the possibility of compensation, since the law does not clearly regulate this point.
To receive money, you need to submit an application indicating the amount and period for which they are issued, or obtain an order from the manager (another person with authority) for such a payment.
Important! If the transfer is made to a personal bank card, then you should obtain the consent of the accountable person for such an operation. For example, when submitting an application for salary transfer, include in the text the phrase: “I ask you to transfer wages and other income, as well as accountable funds to my bank card.”
First we spend - then we receive
The tax office at one time actively equated the reimbursement of money spent in the interests of the company to a sale. In the understanding of the state, the employee sold goods to the employer, and personal income tax had to be withheld from him, and VAT had to be charged to the company (for OSNO) and included in the tax base (for OSNO and simplified tax system). Nowadays such situations are much less common.
Ideally, for such purchases, you should be asked to provide a memo indicating the reasons that prompted the employee to spend his own funds. Of course, few people do this; it is enough to get the report approved by the boss and we can say that the management recognized the costs as justified.
Corporate card - an accountant's headache
The reason that accountants' teeth clench at the mention of a corporate card is simple: it is mainly used by managers. It is not easy to prove to the director - the only participant or owner of the majority of the assets - that the funds in the company account and his personal ones should be separated. Out of habit, the boss uses the corporate card as a simple debit card, including for personal needs.
Considering that the card is special and payments on it are reflected directly in the statement, it is necessary to correctly document the costs. There are two options for this.
The first is when you have constant access to the bank, statements are posted every day and you can control the movement of funds:
- D 55 K 51 (analytics is carried out for each card and user) – we reflect the transfer of money to the corporate card;
- D 71 K 55 – reflect the transferred funds to the accountable person;
- D 20, 26, 44, 60, 76 K 71 (depending on the type of expense) – the report was received and approved.
Second, when it is not possible to track the movement of money promptly, there is no bank data on payments:
- D 71 K 57 – we reflect the money “in transit”, i.e. the employee received and spent them, but this is not yet reflected in the statement;
- D 20, 26, 44, 60, 76 K 71 – we approve the costs according to the report;
- D 57 K 55, D 55 K 51 – the money transfer or withdrawal operation was recorded in the bank statement.
Whoever uses the corporate card must provide supporting documents: checks, invoices, receipts, acts, etc. It would be good if they were issued to an organization, and not to a private individual – the accountable person.
It’s true to warn the seller that payment is not made with a regular debit card; they usually forget and just take cash receipts to the accounting department (we’ll talk about the features of online cash registers below). Can such expenses be taken into account? Yes, you can, in this case everything happens by analogy with ordinary accounting calculations.
Note! If purchases or services are paid for under an agreement concluded with a company, then the documents are drawn up for it, and not for an individual.
The deadline for submitting an advance report on a business trip is no later than 3 working days after returning from it. For other cases, the time is limited to the same three working days, but the countdown starts from the end of the period for which the funds were issued. The latter is set by the manager, which means it can be a month, two, or a year.
Until August 2022, it was necessary to report for the previous advance in order to receive the next one. Violation was followed by a fine of up to 50,000 rubles for an organization and up to 5,000 rubles for an official. Afterwards, one of the paragraphs of Directive No. 3210-U was removed, and penalties no longer apply.
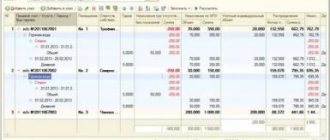
Reflection of an advance report on fuel and lubricants in the 1C Accounting 8 program
Often, at enterprises that have their own vehicles, drivers are not given fuel, but money to buy it. In accounting, this procedure is reflected in the advance report transaction.
In the program 1C: Accounting 8 edition 3.0. First, the issuance of accountable funds is formalized. If the driver receives money for gasoline at the cash register, then a “Cash Withdrawal” document is created in the cash register journal. The program will offer several types of transactions; the cashier must select “Issue to an accountable person.” The document specifies the basis for issuance, the amount and details of the recipient. We carry out this cash withdrawal using Account Debit 71.01 and Account Credit 50.01. In the first tab of the advance report, which will be created in the “Bank and Cash Office” tab, you must fill in the name of the document with which we issued the advance to our accountable driver, the purpose of the advance and the number of attachments to the report.
In the second tab “Goods” of the advance report, we will already reflect the receipt of diesel fuel or gasoline. The name of the supplier, price, type and brand of fuel and how much was purchased are also required. An invoice may be attached to the report. Then in the report itself you will need to indicate the date of its issue and number. Fuel must be received on account 10.03., which is indicated in the nomenclature. Don't forget to check this. Then, according to the document, we will generate the posting Debit 10.03, Credit 71.01. In the event that it is necessary to indicate VAT, we will also carry out the debit of the account on 19.03.
In the event that our driver has not spent all the money given to him on fuel, he returns the rest to the cashier. The cashier registers “Cash receipt”, the type of transaction selects “Return from an accountable person”. It happens the other way around. There wasn't enough money, so the driver invested his own. Then the cashier pays the difference using the document “Cash Withdrawal”, with the type of operation “Issue to an accountable person”. The basis for both documents will be our expense report.
When the time comes to write off the fuel purchased for cash for production, the accountant must create a document “Request-invoice”, which is created, accordingly, on the “Production” tab. The invoice must include what exactly was purchased and how much. You must also assign a write-off account. If fuel was purchased for the main production, then the posting will go to account 20, if the enterprise is a trading enterprise, then 44.01, if gasoline was used for the enterprise’s own needs, then account 26.
About online cash register receipts and more
By bringing a pile of checks to the accountant and leaving him to deal with the papers, employees forget that they should not only receive the documents, but also check their compliance with the law and internal requirements. The accountant will not accept incorrectly documented expenses, the manager will not approve them, which means they will not be reimbursed.
Let's look at the most common mistakes
- Deadline missed. The employer can withhold from the salary the amount of advance payment issued for a business trip and not only (according to Article 137 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- The expenses claimed by the employee are not related to work . It all depends on the specifics of the activity: for an advertising agency, the purchase of a teddy bear can be justified by filming a promotional video, but the same purchase for a shop at a steel smelting plant is unlikely to be justified.
- There is no documentary evidence . The report indicates, for example, the work of a truck crane; a private contractor was hired to carry it out, with whom they did not enter into an agreement and did not provide any documents. There is nothing to confirm the expenses, which means the organization cannot reimburse them.
- Incorrect calculation of daily allowance . Here, errors arise both in the number of business trip days for which payments are due, and in the amounts.
- Incorrect documentation . Common mistakes - incorrect filling, lack of required details, wrong form selected.
Important! This can be done if the employee agrees with the basis and amount of the deduction. The time for management to make a decision to withhold the debt is only 1 month from the date of expiration of the period for repayment of the advance.
Let's take a closer look at the last point. At the very beginning, we mentioned the data that should be in the expense report. Most of them are the required details: the name of the organization or the full surname, name and patronymic of the individual entrepreneur, name and date of the document, full name, signatures, positions of responsible persons, the essence of the business transaction, cost and quantitative expression of indicators. First of all, the availability of this data is checked - something is missing, which means it needs to be re-formatted or supplemented.
In addition, online cash register receipts must contain other details, for example:
- information about the taxation system;
- calculation attribute (receipt, expense, return of receipt, etc.);
- address of the OFD website where you can check the authenticity of the check;
- QR code;
- buyer's phone number or email (if an electronic check is sent);
- place of settlement (address of the building, legal address of the company, website).
Important! In the summer of 2022, new details were added to those listed above. If we are talking about making payments between individual entrepreneurs and/or companies, when bank cards or cash are used, then the check must indicate such data as the name (full name for individual entrepreneurs) and TIN of the buyer, information about the product (country, excise taxes, customs declaration).
Incorrectly completed documents include those in which:
- arithmetic errors were made ( example: the receipt indicates the quantity of goods - 3 pieces, the price - 20 rubles, and the amount - 80);
- corrections were made incorrectly ( example: a number on a sales receipt was filled in by a proofreader, another one was written on top, but it was necessary to cross it out, make the correct inscription and certify it with the seller’s signature, or simply write out a new product receipt);
- There were errors in the details ( example: the old legal address is indicated).
As for the form. The most common is to issue a document that does not correspond to the essence of the transaction. For example, a sales receipt is issued for services rendered instead of an act.
Exceptional cases include the appearance of counterfeits. They are not easy to recognize. Let's say checks with all the necessary details and fiscal data are presented to the accounting department. During an on-site inspection, the Federal Tax Service inspector decides to verify the authenticity of the checks. It turns out that there were no counterparties with the specified tax identification numbers. The checks were issued by a shell company that earned money in this way.
It happens that employees bring documents with a different city indicated on the stamp or in the details. It’s clear that if we’re talking about a business trip to that area, no questions arise. If the employee has not traveled anywhere, check the company indicated on the check through the free service of the Federal Tax Service.
In 2022, and indeed in recent years, with the development of various cashback services and bonus programs, employees make one fatal mistake - they pay for a purchase for work purposes with points accumulated on a personal discount card. Naturally, the payment is displayed in the check as payment with bonuses; the organization cannot reimburse these costs.
Employee advance report for the purchase of fuel and lubricants
Fuel and lubricants are accounted for in account 10.03.1 “Fuel in warehouse” at the actual cost of their acquisition (procurement) or accounting prices (1C chart of accounts).
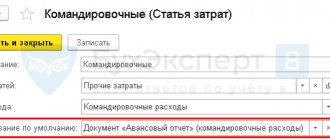
To register an employee's advance report on purchased fuel and lubricants, create the Advance report document in the Bank and cash desk - Cash desk - Advance reports section.
In the header of the document please indicate:
- Warehouse is a place where fuel and lubricants are stored. In this example, it will be the car’s gas tank, since fuels and lubricants are immediately filled into the car. Therefore, a similar name for the storage location of fuels and lubricants is entered into the Warehouses - the name (state number) of the car.
On the Advances , add an advance payment document.
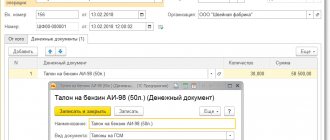
On the Products , provide information about purchased fuels and lubricants and primary documents:
- Document (expense) - the primary document on the basis of which fuel and lubricants are invoiced; in our example, this is a cash register receipt.
- Nomenclature - name of fuels and lubricants, selected from the Nomenclature directory.
If VAT is highlighted on a separate line in the cash register receipt:
- VAT rate - the VAT rate indicated on the cash register receipt.
- SF checkbox .
- the invoice details , as invoices are not issued for retail sales.
Even if VAT is highlighted in a cash register receipt, without an invoice, VAT cannot be deducted (clause 2 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). VAT not accepted for deduction must be written off as expenses that do not reduce the taxable base for profit (clause 1 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated January 24, 2017 N 03-07-11/3094).
Read more about deducting VAT on a cash receipt and accounting for tax expenses
Postings according to the document
The document generates transactions:
- Dt 10.03.1 Kt 71.01 - fuel and lubricants according to the advance report.
- Dt 19.03 Kt 71.01 - VAT on the advance report.
- Dt 91.02 Kt 19.03 - write-off of VAT on other expenses.
- Dt NE.01.9 - expenses not taken into account in the NU.
Documenting
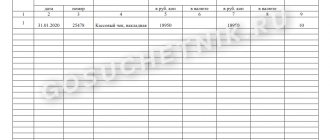
The organization must approve the forms of primary documents, including the form of the advance report. In 1C, an Advance report is used in the form “AO-1”. The completed document can be printed by clicking the Print button - Advance report (AO-1) of the document Advance report . PDF
See also:
- Purchase of fuels and lubricants: legislation and 1C
- Through an accountable person through a corporate card
- By coupons. Transfer of ownership upon refueling
Did the article help?
Get another secret bonus and full access to the BukhExpert8 help system for 14 days free of charge
Related publications
- Purchase of fuels and lubricants by an accountable person through a corporate card Purchasing fuels and lubricants through an accountable person by bank transfer involves the use...
- How to keep a sales book when selling services to individuals for cash The rules for filling out a sales book when selling services to individuals are explained...
- Purchase of fuels and lubricants: legislation and 1C The purchase of fuels and lubricants (fuels and lubricants) has its own characteristics. Purchasing fuel can...
- Purchase of fuels and lubricants using a fuel card with additional charges. expenses...