Step-by-step instruction
Attention! The VAT rate has been changed from 01/01/2019 from 18% to 20% and from 18/118 to 20/120.
An organization conducting trading activities entered into an agreement with KONTUR LLC to create a website, the exclusive rights to which will belong to the Organization. The site is planned to be used as an online store for 10 years.
On February 27, a certificate was signed for work completed on the complete development of the site in the amount of 141,600 rubles. (including VAT 18%).
On February 28, the acquired site was put into operation.
The accounting policy for accounting and financial statements provides for the calculation of depreciation using the straight-line method for all intangible assets.
This example considers the acquisition of a ready-made intangible asset.
Let's look at step-by-step instructions for creating an example. PDF
| date | Debit | Credit | Accounting amount | Amount NU | the name of the operation | Documents (reports) in 1C | |
| Dt | CT | ||||||
| Acquisition of intangible assets | |||||||
| February 27 | 08.05 | 60.01 | 120 000 | 120 000 | 120 000 | Accounting for a non-current asset | Receipt of intangible assets |
| 19.02 | 60.01 | 21 600 | 21 600 | Acceptance for VAT accounting | |||
| Registration of SF supplier | |||||||
| February 27 | — | — | 141 600 | Registration of SF supplier | Invoice received for receipt | ||
| Commissioning of intangible equipment | |||||||
| 28th of February | 04.01 | 08.05 | 120 000 | 120 000 | 120 000 | Commissioning | Acceptance of intangible assets for registration |
| Acceptance of VAT for deduction on intangible assets | |||||||
| 28th of February | 68.02 | 19.02 | 21 600 | Acceptance of VAT for deduction | Generating purchase ledger entries | ||
| — | — | 21 600 | Reflection of VAT deduction in the Purchase Book | Purchase Book report | |||
| Depreciation calculation | |||||||
| March 31 | 44.01 | 05 | 1 000 | 1 000 | 1 000 | Depreciation calculation | Closing the month - Depreciation of intangible assets and write-off of R&D expenses |
| Recognition of depreciation costs as part of commercial (indirect) expenses | |||||||
| March 31 | 90.07.1 | 44.01 | 1 000 | 1 000 | 1 000 | Recognition of depreciation costs as part of commercial (indirect) expenses | Closing the month - Closing account 44 “Costs of distribution” |
In which accounts should intangible assets be recorded?
The accounting account for an intangible asset depends on the right under which it was obtained.
| Right | Account | Example |
| Exclusive right | 0 102 XN 000 “Scientific research (research development)” 0 102 XR 000 “Experimental design and technological development” 0 102 XI 000 “Software and databases” 0 102 XD 000 “Other intellectual property” | Exclusive right to software - account 0 102 ХI 000; Exclusive right to a selection achievement - account 0 102 ХN 000; Exclusive right to a trademark - account 0 102 ХD 000; Exclusive right to an invention - account 0 102 ХN 000 |
| Non-exclusive right | 0 111 6N 000 “Rights to use scientific research (research developments)” 0 111 6R 000 “Rights to use experimental design and technological developments” 0 111 6I 000 “Rights to use software and databases” 0 111 6D 000 “Rights to use other objects of intellectual property" | Non-exclusive right to antivirus - account 0 111 6I 000; Non-exclusive right to a utility model - account 0 111 6N 000; Non-exclusive right to an electronic archive - account 0 111 6I 000; Non-exclusive right to a literary work - account 0 111 6D 000. |
Objects of intangible assets are grouped according to clause 37 of Instruction No. 157n. That is, objects received under exclusive right are accounted for in the corresponding account 102 00, where X can take the value 2 “Especially valuable movable property of the institution”, 3 “Other movable property of the institution” or 9 “Property in concession”.
More on the topic: Property accounting in 2022: 10 “hot” questions
For example, on account 102 91 “Software and databases in concession” information about programs for electronic computers, databases, information systems and (or) sites on the Internet or other information and telecommunication networks that are the objects of concession agreements is subject to reflection. which includes such computer programs and (or) databases, or about the totality of these objects, as well as about operations that change them.
The grouping by type of property, designated by the letters N, R, I or D, corresponds to the subsections of the classification established by OKOF *(3) (clause 67 of Instruction No. 157n, letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 17, 2020 No. 02-07-10/81813). Namely, OKOF provides for the following groups of intellectual property objects (OKOF code 700):
- scientific research and development (OKOF code 710);
- software and databases (OKOF code 730);
- other objects of intellectual property (OKOF code 790).
For example, multimedia applications are named in the “Software and Databases” group - OKOF code 732.00.10.08. Consequently, the exclusive right to this object, related to other movable property, is taken into account in account 102 3I. And if an institution has a non-exclusive right to multimedia applications, then it will be reflected in account 111 6I.
Acquisition of intangible assets
The organization's expenses in property, which will subsequently be accepted in accounting as an intangible asset, are accounted for in account 08.05 “Acquisition of intangible assets” (1C chart of accounts).
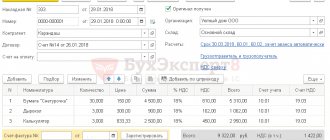
The acquisition of intangible assets is reflected in the document Receipt of intangible assets in the section Fixed assets and intangible assets - Intangible assets - Receipt of intangible assets.
The document states:
- Intangible asset - an intangible asset from the directory Intangible Assets ;
- Type of object - Intangible asset ; PDF
- Accounting account - 08.05 “Acquisition of intangible assets”;
- VAT account - 19.02 “VAT on acquired intangible assets.”
Postings according to the document
The document generates transactions:
- Dt 08.05 Kt 60.01 - capitalization of intangible assets;
- Dt 19.02 Kt 60.01 - acceptance of VAT accounting.
Registration of SF supplier
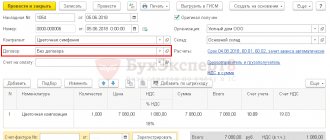
To register an incoming invoice from a supplier, you must indicate its number and date at the bottom of the Receipt (act, invoice) , and click the Register . PDF
The Invoice document received is automatically filled in with the data from the Receipt document (act, invoice) .
- Operation type code : “Receipt of goods, works, services.”
Regardless of whether the Reflect VAT deduction in the purchase book by date of receipt , when this is done, no entries will be made to accept VAT for deduction. Deduction of VAT on intangible assets is possible only through the document Formation of purchase ledger entries .
Commissioning of intangible equipment
Intangible assets used in the organization are accounted for in the debit of account 04 “Intangible assets” (chart of accounts 1C) at their original cost. The initial cost of intangible assets is formed based on the actual costs of its acquisition and other expenses directly related to the acquisition and provision of conditions for using the asset for the intended purposes, with the exception of VAT and other refundable taxes (clauses 6-8 PBU 14/2007, clause 3 Article 257 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Learn about the formation of the initial cost in BU and NU
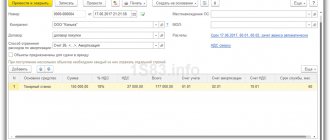
Acceptance for accounting of intangible assets is formalized by the document Acceptance for accounting of intangible assets in the section Fixed assets and intangible assets - Intangible assets - Acceptance for accounting of intangible assets.
Non-current asset tab
On the Non-current asset , the data of the acquired asset before commissioning is indicated:
- Type of accounting object - Intangible asset ;
- Method of receipt - the method of receipt of a non-current asset into the organization, in our example it is Purchase for a fee ;
- Intangible asset - a previously entered intangible asset in the Intangible Assets ;
- Account - 08.05 “Purchase of intangible assets”.
Click the Calculate amounts to fill in the following fields:
- Price;
- NU cost.
Accounting tab
The cost of intangible assets in accounting is repaid through depreciation. If the useful life of intangible assets is not determined, then depreciation is not accrued (clause 23 of PBU 14/2007).
On the Accounting it is indicated:
- Accounting account - 04.01 “Intangible assets of the organization”;
- Depreciation account - “Amortization of intangible assets”;
- Accrue depreciation checkbox must be checked: it is this that affects the automatic calculation of depreciation in accounting when closing the month;
- The method of calculating depreciation is the accrual method according to the accounting system established in the accounting policy of the organization;
- The method of reflecting depreciation expenses is the method of accounting for the costs of depreciation of intangible assets, selected from the directory Methods of reflecting expenses .
In our example, costs are taken into account according to Dt 44.01 “Costs of distribution in organizations engaged in trading activities” (chart of accounts 1C), since depreciation costs of trading organizations are included in business expenses in accounting (indirect expenses - in NU).
- Useful life (in months) —the estimated useful life.
Tax Accounting Tab
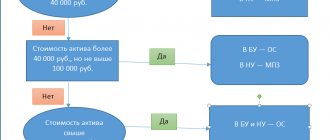
In NU, depreciable property is recognized as property that has (clause 1 of Article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- useful life more than 12 months;
- initial cost more than 100,000 rubles.
On the Tax Accounting the following is indicated:
- The procedure for including cost in expenses is depreciation , because in tax accounting, the asset is recognized as depreciable property;
- Accrue depreciation checkbox must be checked: it is this that affects the automatic calculation of depreciation according to the tax base when closing the month ;
- Useful life (in months) - useful life, according to the established depreciation group of intangible assets;
- A special coefficient is a reduction coefficient if it is established by the accounting policy. In our example, it is not installed, so we do not fill out this field (clause 4 of Article 259.3 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Only reducing factors can be applied to the depreciation rate of intangible assets. Increasing coefficients (clauses 1-3 of Article 259.3 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) are provided exclusively for OS.
Postings according to the document
The document generates the posting:
- Dt 04.01 Kt 08.05 - commissioning of intangible equipment.
Creating an Asset
If an intangible asset is created in an institution, then the initial cost of the property should include:
- Remuneration of workers involved in the creation of the facility. Please note that not only accrued wages are taken into account, but also insurance premiums and other deductions from wages.
- Costs of payment for work, services, goods purchased to create intangible assets. Including under author's order agreements or GPC agreements.
- Institutional expenses for maintenance, repair and operation of equipment used in the creation of intangible property.
- Other categories of expenses of the organization.
It is unacceptable to include the following expenses in the initial cost:
- General business expenses, except for costs directly related to the development of intangible assets.
- The organization's expenses for research, technological and development work of previous reporting periods, which have already been recognized as income and expenses.
- Expenses directly related to the creation of samples of new products accepted into the NFA of the institution only based on the results of technological, research and development work.
Charge the costs to accounting account 0 106 00 000 in the same manner.
Acceptance of VAT for deduction on intangible assets
VAT is accepted for deduction on purchased intangible assets if the following conditions are met (clause 2 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- Intangible assets must be used in activities subject to VAT;
- a correctly executed SF (UPD) is available;
- Intangible assets were accepted for accounting on account 08.05 “Acquisition of intangible assets” (paragraph 3 of clause 1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Ural District dated December 25, 2013 N F09-13315/13 in case N A76-25197/2012).
VAT can be deducted within 3 years after it is registered in account 08.05 “Acquisition of intangible assets”. In this case, VAT must be deducted on intangible assets in the full amount of tax indicated in the invoice (clause 1, 1.1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 19, 2017 N 03-07-11/84699).
At the moment, in 1C, accepting VAT for deduction is possible only after reflecting intangible assets on account 04.01 “Intangible assets of the organization”, i.e. after posting the document Acceptance for accounting of intangible assets . Unlike OS, this may pose a tax risk.
Due to the fact that the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, in order to accept VAT for deduction, does not indicate in which accounting account the object of intangible assets should be accounted for, disagreements between tax authorities and taxpayers cannot be ruled out regarding the issue of counting the 3-year period for claiming this deduction - by analogy with the deduction VAT on fixed assets (Definition of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated September 21, 2015 N 309-KG15-11146). Regarding intangible assets, such judicial practice is not enough to draw any conclusions.
Acceptance of VAT for deduction on intangible assets is formalized by the document Generation of purchase ledger entries in the Operations section - Closing the period - Regular VAT operations. To automatically fill out the Purchased Assets , you must use the Fill .
Postings according to the document
The document generates the posting:
- Dt 68.02 Kt 19.02 - VAT accepted for deduction.
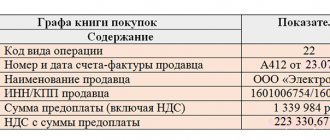
Purchase Book report can be generated from the Reports - VAT - Purchase Book section. PDF
VAT declaration
The deduction amount is reflected in the VAT return:
In Section 3 page 120 “Amount of VAT to be deducted”: PDF
- the amount of VAT accepted for deduction.
In Section 8 “Information from the purchase book”:
- invoice received, transaction type code "".
Rules for accounting for intangible assets
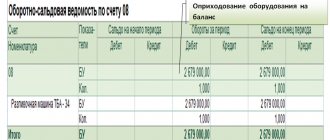
Information on account 04 consists of the cost of all inventory items recorded on the balance sheet (at initial or actual cost). The account is active: receipts are reflected as a debit, and write-offs as a credit.
Objects are accepted for accounting through account 08 “Investments in non-current assets”. At this stage, the initial cost of the asset is formed and it is debited to account 04 immediately after it is ready for operation. This happens after checking the object for compliance with all the requirements prescribed in the PBU for intangible assets (link above).
Depreciation calculation
Regulatory regulation
In accounting, the cost of intangible assets is repaid through depreciation, starting from the next month after the object is accepted for accounting and ceases to be repaid from the next month after its disposal or full repayment of the cost of intangible assets (clauses 31-33 of PBU 14/2007).
Depreciation is calculated on the credit of the “Amortization of intangible assets” account in correspondence with cost accounts. In our example, intangible assets are taken into account for commercial needs, therefore, the costs of accrued depreciation are charged to distribution costs in the debit of account 44.01 “Costs of distribution in organizations engaged in trading activities” (1C chart of accounts).
In tax accounting, the cost of an intangible asset is repaid through depreciation, starting from the next month after its commissioning and ceases to be repaid from the next month after its disposal or full repayment of the cost (clause 4 of article 259 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 5 of article 259.1 of the Tax Code RF).
In NU, accrued depreciation may be recognized as part of direct, indirect or non-operating expenses, in accordance with the accounting policy for NU. In our example, depreciation is taken into account as part of indirect expenses at a time on the last day of the accrual month.
Find out more about the features of calculating depreciation in 1C
Accounting in 1C
The parameters for calculating depreciation are set:
- initially - in the document Acceptance for accounting of intangible assets;
- if there is a change in the parameters for reflecting depreciation, see the document Changing the reflection of depreciation of intangible assets .
Monthly depreciation is calculated when performing the procedure Closing the month operation Depreciation of intangible assets and writing off R&D expenses in the section Operations - Closing the period - Closing the month.
In our example, the website www.udom-shop.ru was accepted for accounting as intangible assets and put into operation on February 28, therefore, depreciation in accounting and accounting records is accrued from March.
Postings according to the document
The document generates the posting:
- Dt 44.01 Kt - depreciation.
Similarly, depreciation is calculated for the following months until the cost is fully repaid. When disposing of intangible assets, depreciation for the last month is accrued in the disposal document, for example, in the document Transfer of intangible assets .
Control
Depreciation calculation:
The monthly depreciation amount in 1C is calculated correctly.
Documenting
The organization must approve the forms of primary documents, including documents for calculating depreciation, for example, an Accounting Certificate.
In 1C, you can print a depreciation calculation form using the Help-calculation of depreciation in the Operations section - Closing the period - Closing the month - button Help-calculation - Depreciation.
It presents the calculation of depreciation in BU PDF and NU PDF separately, but with the ability to disclose the amount of depreciation by month of accrual.
Depreciation
The depreciation of intangible assets in accounting has changed significantly: assets with an indefinite useful life are no longer depreciated. Previously, such objects had a ten-year useful life. In 2022, it is required to revise the SPI for these intangible assets. If the commission classifies them as objects with an indefinite life, then depreciation on them stops.
IMPORTANT!
Do not adjust the depreciation amount from previous years. In the NFA accounting card in form 0504031, it is necessary to change the information about the useful life and the depreciation procedure (Letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 02-07-07/25218 dated 04/02/2021).
Depreciation is charged only on assets with a certain SPI. If the cost of the object does not exceed 100,000 rubles, 100% depreciation is charged when recognizing the object as part of the intangible assets group. There are no special rules for calculating depreciation on intangible assets with a non-exclusive right of use.
Recognition of depreciation costs as part of commercial (indirect) expenses
When closing the month, depreciation on account 44.01 “Distribution costs in organizations engaged in trading activities” is written off in full to account 90.07.1 “Sales expenses for activities with the main taxation system” (chart of accounts 1C).
In order for distribution costs to be reflected as part of sales expenses, it is necessary to run the procedure Closing the month, operation Closing account 44 “Distribution costs” in the section Operations - Closing the period - Closing the month.
Postings according to the document
The document generates the posting:
- Dt 90.07.1 Kt 44.01 - reflection of distribution costs in the amount of depreciation as part of business expenses.
Income tax return
The amount of accrued depreciation is reflected in the income tax return: PDF
In Sheet 02 Appendix No. 2:
- page 040 “Indirect costs – total”;
- page 131 “Amount of depreciation..., accrued using the straight-line method”: page 132 “incl. on intangible assets." For information
To access the section, log in to the site.
See also:
- Accounting policy: intangible assets
- Functionality: OS and NMA
- VAT deduction when creating intangible assets
Did the article help?
Get another secret bonus and full access to the BukhExpert8 help system for 14 days free of charge
Related publications
- Acceptance for accounting of a fixed asset with a depreciation bonus. Along with depreciation, the organization has the right to include one-time expenses that reduce...
- Document Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets The acquisition of equipment, movable and immovable property is almost always associated with...
- Document Acceptance for registration of intangible assets The document Acceptance for registration of intangible assets is intended for registration…
- Document Acceptance for registration of intangible assets under the simplified tax system The document Acceptance for registration of intangible assets is intended for registration…
Features of accounting for intangible assets under the simplified tax system.
Of course, not all telecom operators have the right to use the simplified tax system due to non-compliance with the criteria established by Chapter. 26.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (in terms of income, number of employees, residual value of fixed assets, company structure and participation in their authorized capital of other legal entities). Meanwhile, the fiscal attractiveness of this special regime (if we are talking about the object of taxation “income minus expenses”) is partly offset by the closed list of expenses recognized in the tax base. In addition, some tax rules are not clearly stated. For example, the initial cost of a characteristic intangible asset object, software, created by a telecom operator using the simplified taxation system, is formed on the basis of the actual costs of its creation (manufacturing). Expenses for intangible assets include, among other things, labor costs (including insurance premiums). But the concept of “labor costs”, according to the current legislation, equally covers both payments made by the telecom operator to employees directly for performing a labor function, including those related to the creation of an intangible asset (software), and payments not directly related to work activity, but calculated on the basis of average earnings, for example vacation pay. Consequently, vacation pay (and insurance premiums accrued on them) can be classified as a risky expense for “simplified” people. How to deal with such costs: include intangible assets in the initial cost or record intangible assets as an independent expense? Based on the explanations of official bodies and judicial practice, we will try to answer this question.