How to get back overpayment of overpaid taxes
If an organization or individual entrepreneur has discovered that the amount of taxes has been overpaid, then there are two possible scenarios: return the funds to your current account, or offset the excess to another tax (KBK).
Procedure for refund
If an organization decides that the overpaid tax must be returned back to the current account rather than offset, a special application for a tax refund is drawn up for this purpose.
A special KND form 1150058 has been developed for it. It was updated in 2022, and is currently more reminiscent of a declaration. The application must indicate the name of the company, the amount of overpayment, the BCC for the tax, and the details of the taxpayer’s current account.
The completed document is submitted to the Federal Tax Service in several ways:
- In paper form personally by the taxpayer or his representative by proxy;
- By post with notification of receipt;
- In electronic form via the Internet, but an electronic digital signature will be required.
The process of refunding excess tax can be divided into several stages:
- Determine that an overpayment has occurred. This can be done, for example, by requesting a tax reconciliation report from the Federal Tax Service. The document will show for what tax and in what amount the excess transfer of funds occurred.
- Submit a return application. In it you need to indicate information about the company, the amount to be returned and the details of the bank account to which this should be done;
- Submit the application to the tax office in person or through a representative, by mail or via the Internet;
- After 10 days, receive the result of the application review. If the authority unlawfully refuses a return, prepare documents to transfer the case to court;
- Within a month from the date of filing the application, the Federal Tax Service must return the funds to the current account;
- If the time has expired, but enrollment has not been made, write a complaint to a higher inspection and prepare documents to transfer the case to court.
How to offset overpaid tax
If the taxpayer decides not to make a refund of overpaid tax, he can offset it:
- For further payment of the same tax;
- To pay off a debt for another unpaid tax.
When performing an offset, you must follow the rule - a payment can only be offset within the budget of the same level. Those. an overpayment for a federal tax will be credited only to another federal one, for a regional tax - to another regional one, etc.
The Federal Tax Service has the right, if an overpayment is detected, to independently offset the underpayment of another tax. In this case, the company's consent is not required.
To make an offset, you must submit an application for tax offset using a special form KND 1150057.
This can be done in three ways:
- On paper in person or through a representative;
- By post;
- Through Internet services.
Attention! The offset can be made within 3 years from the date of the overpayment.
How to write off tax overpayments as non-operating expenses
One of the mandatory conditions of an employment contract is the place of work. However, the Labor Code does not explain exactly how it should be indicated. In practice, someone gives the name of the organization, someone in addition reflects its location, that is, the address. As a result, disputes often arise - between the employee and the employer, between the employer and regulatory authorities. How to avoid mistakes? Let's figure it out. After preparing financial statements, institutions need to prepare public disclosure of their indicators. In particular, from 2022, mandatory general requirements for the minimum composition and procedure for presenting such information are established in the Federal Accounting Standard for Public Sector Organizations “Presentation of Accounting (Financial) Statements”, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 31, 2016 No. 260n.
Please note => How to use maternity capital in 2022
All comments (3)
Good afternoon, Olga. It is necessary, first of all, to find the reason for the discrepancy with the budget, and then make adjustments to the accounting. What taxes are not reconciled with the budget? After receiving the reconciliation report, if there are discrepancies, you return the reconciliation report to the Federal Tax Service, indicating the amounts according to your data. Having received from you an act with discrepancies, tax authorities must create Section II of this act, where your accruals and those transferred to the budget will be indicated in detail.
Good afternoon, Olga. Ideally, you need to look for errors that cause disagreements with the Federal Tax Service Inspectorate, but if this is not possible, then you can do the following: If I understand correctly, you signed a joint reconciliation report with the Federal Tax Service Inspectorate without disagreement, which means you agreed with the data of the tax authority and admitted the errors in your accounting If you are a small business entity, then you have the right to correct significant and insignificant errors of previous years at the time of discovery and take them into account as part of other income and expenses. Therefore, you can correct the error in calculating taxes of previous years by posting: - Accounts receivable - Dt 91.02 Kt. 68; — Creditor’s — Kt 91.01 Dt 68
Access to the “Ask a Question” form is only possible if you have fully subscribed to BukhExpert8. Submit an application on behalf of Legal Entity. or Phys. faces you can here >>
By clicking the “Ask a Question” button, I agree to the BukhExpert8.ru regulations >>
General rules for offset and refund of overpayments
The following points are common to the offset and refund of overpayments for income tax:
- Offset and refund can be made within a period of no more than 3 years from the date of the overpayment (clause 7 of article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- For overpayments resulting from filing a declaration, offset and refund will be possible only after 3 months allotted to the tax authorities to verify the declaration (clause 2 of Article 88 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated February 21, 2017 No. 03-04-05/ 9949).
- Offset and return are carried out on the basis of an application submitted to the Federal Tax Service in the approved form (clauses 4 and 6 of Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The application can be sent electronically or submitted to the Federal Tax Service on paper. In the latter case, it is made in 2 copies.
Application forms for refund and offset of overpayments of taxes can be downloaded from our website: “Form and sample application for tax offset” and.
Find out how to fill out an application for a refund of overpaid taxes using KND form 1150058 in ConsultantPlus. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial online access for free.
- Before submitting an application for a credit or refund, an organization must check the amount of the existing overpayment with the data of the tax authorities. It is not necessary to do a reconciliation for this. It is enough to request a certificate from the Federal Tax Service about the status of settlements with the budget and make sure that the overpayment amounts match. This must be done due to the fact that tax authorities have the right to independently offset the overpayment to pay off arrears on other taxes (clause 5 of Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
For information on the procedure for conducting an inventory of payments, see the article “Inventory of receivables and payables.”
- The decision to carry out such an offset (or to refuse it) must be sent to the organization in writing within 5 working days from the date of its adoption (clause 9 of Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
What to do if the tax was written off by mistake
The tax office has the right, without the approval of the taxpayer himself, to withdraw from him unpaid amounts of taxes, fines or penalties.
Sometimes such actions are carried out by mistake - for example, the authority did not receive a payment order, or the taxpayer himself made a mistake and indicated the wrong details, BCC number, etc.
If such an event does occur, then the tax office is obliged to return the unlawfully withheld amount. If the company has debts for any other taxes, then part of this payment can be used to pay them off, and the remaining funds will be returned.
To make a refund, you must submit a written application in free form to the Federal Tax Service. It must state the circumstances of the case, attach a supporting document (payment with tax transfer), and indicate bank details for the refund.
bukhproffi
Important! The application must be submitted within 1 month from the date of the unlawful write-off. If this period is missed, the amount can only be returned through legal proceedings.
Three years are allotted for this.
It takes 10 days to process the submitted application. Next, the authority is given 1 month to return the amount to the bank account.
Taxes and Law
The amount of overpaid tax is subject to refund upon a written application from the taxpayer. If he has arrears on the same budget, the refund of the overpaid amount is made only after the specified amount is offset against the arrears. With regard to overpayments by persons who have ceased their activities, the Federal Tax Service explains the following. The Tax Code does not prevent the write-off of such amounts if the taxpayer is notified of them in the prescribed manner, if they are not required to be used to repay arrears on other taxes, fees, penalties, fines, if the taxpayer did not apply for the return (offset) of these amounts, did not carry out financial - economic activities and did not submit accounting and tax reports to the tax authorities, according to which it was possible to offset the amount of overpaid tax against upcoming payments.
24 Dec 2022 marketur 371
Share this post
- Related Posts
- Law on providing unpaid leave to working veterans of the Chelyabinsk region
- What is the punishment for bakers for harmful working conditions?
- Statement of claim to the court for a lump sum payment of the funded part of the pension
- Transport tax benefit for pensioners in 2022 in the Sverdlovsk region
Tell me about the postings, to calculate the overpayment of tax.
then the tax office returns to us the overpayment of the simplified tax system, due to the fact that we are on OSNO.
What kind of restoration wiring should I do for this operation?
68.12 76.2 (claims) USN 51 68.12 returned the tax to the Federal Tax Service.
account balance hangs at 76.2
The reconciliation report revealed an overpayment of VAT that was not accounted for in used accounts. How can I reflect this overpayment now?
once again, at the beginning of the year there is a CD of 68.12 100,000, then you paid this CD 68.12 51,100,000
then I wrote a letter to the tax office about reviving the simplified tax system, as we had lost it.
The tax office returns 51 68.12.
but before that we must have wiring and what it is.
they recommend 76.2.
overpayment as a result of real overpayment, since the shaggy times. BUT when entering the initial balances into the program, I did not take this overpayment into account.
and now I don’t know which wiring to consider..
Where did she go? The balance probably wouldn’t balance without her.
then the zero one will not close. Then I need to reduce 76 by this amount?
thanks for answers. I have already handed over the balance. Then tell me how to correct the situation so that everything will be normal in the year.
According to DT 76 I have a surplus amounting to 311,000 rubles. for the beginning of the year. I still removed this overpayment for 68 from 76, because initially the balances paid at the beginning of the year were overstated on the liability for CT 68 by this amount.
that is, if at the beginning of the year I had immediately put the simplified tax system for CT 68 into an overpayment of 182,000, then for DT 76 (excess) it would have been less by this amount.
so now, since I adjusted the 76th (68 76), on DT 76 the amount is 129,000.
What corrections do I need to make now to make everything right?
76 91 182 000 (tax return) 91 76 311 000 (surplus at the beginning of the year)
if I had put 91 76 at the beginning of the year (then we would have had a loss in second-hand).
https://youtube.com/watch?v=wrFTIL6tK00
Accounting entry when offsetting money between taxes
The reflection of such transactions in the accounting records of institutions has its own characteristics. There may be several reasons for overpayment of taxes, fees and other obligatory payments, for example, a counting error or invalidation of the tax inspectorate’s decision to collect taxes, fines, penalties, etc. from the institution.
This operation is possible if the companies have obligations to each other with the same amount. For example, you have a debt to the Beta organization in the amount of 100,000 rubles. But we also have obligations to Alpha in a similar amount.
Write off tax debt postings
Has the bank already been liquidated or just at the stage? For now, “forget” about account balances in a bank whose Central Bank license has been revoked. You will not use them for anything - neither to pay taxes and other obligatory payments to the budget, nor at your own discretion. Now in accounting you can transfer them to other property and equipment, and then accrue a reserve for doubtful debts, and after liquidation, write off these receivables at the expense of the created reserve. After the bank is declared bankrupt, write it off the balance sheet as uncollectible and record it in an off-balance sheet account (perhaps you will still be able to receive some money someday). It's not that easy to write off. You need to document that you tried to claim the receivable (debt from the borrower). It also depends on who the borrower is? if an employee, personal income tax must be withheld from him. And if not an employee, then do you have a license to carry out banking operations?
Please note => Consultant plus court decisions defendant Art. 236392 Labor Code of the Russian Federation 870 resolution Sberbank plaintiff employee harmful working conditions benefits and compensation harm to health
Tax accounts
The following accounts are used to reflect transactions related to the calculation, accounting and payment of taxes:
- Account 19 reflects the amount of VAT on material assets acquired by the organization: fixed assets, intangible assets, inventories.
- Account 68 takes into account all payments for personal income tax, taxes on real estate, vehicles, income from transactions with securities, mining, environmental fees, fees for the use of natural resources, etc.
- Account 69 is used to record contributions to social insurance and security, health insurance, and contributions to the Pension Fund.
- Account 90 is intended for accounting for tax payments subject to return (reimbursement) after the sale of products, primarily VAT and excise taxes.
- Account 91 is used to reflect VAT and excise taxes related to sold tangible and intangible assets that were on the balance sheet of the enterprise.
- Account 99 is used to account for the company’s losses, which include paid income tax, penalties, fines for violations of the procedure and deadlines for accrual and payment.
Read more - Article on the payment of various taxes to the budget.
How to write off an old overpayment of income tax (Mislovich A
Accountants quite often encounter the problem of writing off an overpayment of income tax when the three-year period for filing an application for a refund of the overpaid tax has expired. Let's consider the option of writing off such an overpayment, the legality of which, if there is a certain risk, is confirmed by judicial practice. In general, the amount of overpaid tax is subject to offset against the taxpayer's upcoming payments for this or other taxes, repayment of arrears for other taxes, arrears of penalties and fines for tax offenses, or a refund to the taxpayer. An application for offset or refund of the amount of overpaid tax can be submitted within three years from the date of payment of the specified amount (clauses 1, 7, article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Sometimes, in the process of carrying out inventory activities and/or internal audit of a legal entity, overpayments of income tax may be identified, but the deadline for filing an application with the tax authority for the return of such overpaid amounts has already passed. In such a situation, it is possible to write off the overpaid tax for non-operating expenses. An open list of expenses that can be classified as non-operating expenses is given in paragraph 1 of Art. 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The question of the legality of classifying these funds as non-operating expenses has been raised repeatedly in judicial practice. Her analysis points to the option of reflecting the “old” overpayment of income tax as part of non-operating expenses as a bad debt.
Refund of prepayment to the buyer under the simplified tax system
The company may be faced with a situation where the unfulfilled contract under which the advance was received was terminated, for example, due to a significant change in circumstances (Article 451 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation) or by agreement of the parties (Clause 1 of Article 450 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, it is necessary to return the advance payment to the buyer. At the same time, the prepayment return period has a significant impact on the seller’s reporting indicators
In accounting, the received advance is taken into account as part of accounts payable (clauses 3, 12 of PBU 9/99, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 6, 1999 No. 32n) on account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers.” At the same time, the amounts received as prepayment are reflected separately (Instructions for the application of the Chart of Accounts for accounting financial and economic activities of organizations, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n). At the time of repayment of the advance, the specified debt is repaid.
The organization has an overpayment of tax according to the simplified tax system, which arose in 2010
Having considered the issue, we came to the following conclusion: On the date of writing off to the budget the amounts of overpaid tax, from the date of payment of which more than three years have passed, the organization can create the following entry in accounting: Debit 91, subaccount “Other expenses” Credit 68, subaccount “ simplified tax system" - overpayments under the simplified tax system are written off to the budget. Rationale for the conclusion: In accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the amount of overpaid tax is subject to offset against the taxpayer’s upcoming payments for this or other taxes, repayment of arrears for other taxes, arrears of penalties and fines for tax offenses, or refund to the taxpayer in the manner prescribed by this article. In this case, offset and refund of the amount of overpaid tax are made on the basis of the taxpayer’s application (clauses 4, 6, Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In accordance with paragraph 7 of Art. 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, an application for offset or refund of the amount of overpaid tax can be submitted within three years from the date of payment of the specified amount, unless otherwise provided by the legislation of the Russian Federation on taxes and fees. Let us note that the tax authority is obliged to inform the taxpayer about each fact of excessive payment of tax and the amount of overpaid tax that has become known to the tax authority within 10 days from the date of discovery of such a fact (Clause 3 of Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not determine the grounds and procedure for tax authorities to write off overpaid amounts of taxes, fees, penalties and fines, from the date of payment of which more than three years have passed (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 02/11/2013 N 03-02-07/1/3225). At the same time, when a taxpayer applies to a tax authority with a request to write off the specified amounts, including amounts of canceled taxes, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not prevent the tax authority from writing off the corresponding amounts for which the period specified in paragraph 7 of Art. 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 27, 2011 N 03-02-07/1-349, Federal Tax Service of Russia dated November 1, 2013 N ND-4-8 / [email protected] ). It should be noted that if the taxpayer allows an overpayment of tax, the tax base as one of the elements of taxation is distorted. Consequently, an overpaid “tax” - calculated from a distorted tax base - cannot be considered a legally established tax payment. If a taxpayer overpays a certain amount of tax in the current tax period, this amount is subject to all constitutional guarantees of property rights, since its payment in this case was made in the absence of a legal basis. That is, we can conclude that the amount of overpaid tax, for the return of which from the budget the statute of limitations has expired, refers to bad debts (see also the resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated November 28, 2013 N F05-13700/13 in case N A40-155004/ 2012). According to the Instructions for the application of the Chart of Accounts for accounting financial and economic activities of organizations (approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 31, 2000 N 94n) (hereinafter referred to as the Instructions), the amount of overpayment of taxes and penalties is reflected in the accounting records as the debit of account 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees” " At the same time, on the basis of clause 12 of PBU 10/99 “Expenses of the organization” and clause 77 of the order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 29, 1998 N 34n, the amount of receivables for which the statute of limitations has expired, other debts that are unrealistic for collection are other expenses. Such amounts during the reporting period are reflected in the credit of account 91 “Other income and expenses” (Instructions). Taking into account the above, we believe that on the date of writing off to the budget the amounts of overpaid tax, from the date of payment of which more than three years have passed, the organization can create the following entry in its accounting: Debit 91, subaccount “Other expenses” Credit 68, subaccount “USN” - The overpayment under the simplified tax system was written off to the budget.
Please note => How to correctly write sick leave or sick leave
Payment of personal income tax to an employee
Before the tax agent returns from the budget the amount of personal income tax that was excessively withheld and transferred from the taxpayer, he has the right to return the overpayment at his own expense.
Let's look at an example of which entries for personal income tax returns should be drawn up by an accountant.
Example An employee’s taxable income erroneously included the amount of financial assistance paid to him in the amount of 4,000 rubles. As a result, he was overdeducted and transferred to the personal income tax budget in the amount of 520 rubles. (RUB 4,000 x 13%). When this fact was revealed, the employee was returned the overpayment from the travel agency's cash desk, after which she (as a tax agent) received a refund from the budget.
The postings for the return of personal income tax will be as follows: DEBIT 70 CREDIT 68 subaccount “Personal income tax settlements” - 520 rubles. – erroneous entry reversed;
DEBIT 51 CREDIT 68 subaccount “Personal Income Tax Payments” – 520 rubles. - money was returned from the budget.
DEBIT 70 CREDIT 50 – 520 rub. – the money was returned to the employee.
How to return an overpayment of income tax
The text of the application for the return of an overpayment must indicate the details of the current account to which the organization requests to return the amount of the existing overpayment.
The decision on a refund is made by the tax authorities in the same way as for offset, within 10 working days (clause 8 of Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Moreover, if at the time the decision is made, the organization has arrears in payments to the budget of the same level, then such debt will first be repaid from the amount of the existing overpayment (clause 6 of Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The decision of the tax authority will reflect the fact of offset of the existing debt. The remaining overpayment amount will be refunded.
The actual refund of funds is carried out by the Federal Treasury on the basis of instructions from the tax authority. The total return period should not exceed one month from the date of filing the application for return (Clause 6, Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The organization will take into account the fact of the return of funds on the date of receipt of funds by posting to the debit of account 51 from the credit of account 68 (sub-account for accounting for income tax calculations in which the overpayment took place). The offset carried out by the tax authority when making a decision on the return will be reflected in the entries in the same way as when offset on the initiative of the organization.
ConsultantPlus experts explained the nuances of refunding overpayments or crediting income taxes. Study the material by getting trial access to the K+ system for free.
Income tax refund
According to Art. 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the offset of amounts of overpaid federal taxes and fees, regional and local taxes is carried out for the corresponding types of taxes and fees, as well as for penalties accrued on these taxes and fees. For example, an overpayment of income tax can be offset against payment of the same tax or other federal taxes.
The Tax Code does not limit the possibility of carrying out an offset depending on which budget of the budget system of the Russian Federation the federal tax is payable to. Thus, the corporate income tax, which is federal, overpaid to the budget of one subject of the Russian Federation, can be offset against upcoming payments for this tax to the budget of another subject of the Russian Federation, taking into account the provisions of paragraphs 4 and 5 of Art.
78 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
This is not the first time our magazine has addressed this topic. Today we will answer specific questions related to the offset (refund) of overpaid income tax, and also consider the situation with writing off an overpayment for which the deadline for applying for a refund has expired.
See the articles “How to return or offset overpaid amounts of tax”, “Deadline for filing an application for a refund (offset) of overpaid tax”, 2011, No. 2.
Penalties for the period when the tax authority made a decision on offset
By virtue of paragraph 1 of Art. 45 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the taxpayer is obliged to independently fulfill the obligation to pay tax, unless otherwise provided by the legislation on taxes and fees. This obligation must be fulfilled within the period established by law. The taxpayer has the right to fulfill the obligation to pay tax ahead of schedule.
According to paragraphs. 4 p. 3 art. 45, the obligation is considered fulfilled by the taxpayer from the day the tax authority, in accordance with the Tax Code, makes a decision to offset the amounts of overpaid or excessively collected taxes, penalties, and fines against the fulfillment of the said obligation.
The procedure for offsetting amounts of overpaid taxes is established by Art.
Overpayment of income tax
78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, according to clause 1 of which the offset of overpaid federal taxes and fees, regional and local taxes is carried out for the corresponding types of taxes and fees, as well as for penalties accrued on the corresponding taxes and fees.
As a general rule, the Tax Code does not prohibit the offset of taxes in the payment of relevant types of taxes between the federal budget, regional and local budgets. Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 5, 2008 N 92n provides for interregional offset - carried out by tax authorities located in the territories of various constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
“On approval of the Procedure for accounting by the Federal Treasury of revenues to the budget system of the Russian Federation and their distribution between the budgets of the budget system of the Russian Federation.”
The offset of the amount of overpaid tax against the taxpayer's upcoming payments for this or other taxes is carried out on the basis of his written application by decision of the tax authority, which must be accepted within 10 days from the date of receipt of the taxpayer's application (clause 4 of Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The tax authority does not have the right to independently (without the specified application) offset.
For your information. Paragraph 11 of the Information Letter of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated December 22, 2005 N 98 states: the period for offset of the amount of overpaid tax begins to be calculated from the date of filing the application for offset, but not earlier than from the moment of completion of the desk tax audit for the corresponding tax period or from the moment when such verification must be completed in accordance with Art. 88 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Clause 2 of Art. 57 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation determines that when paying a tax in violation of the deadline, the taxpayer is charged penalties in the manner and under the conditions provided for by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Penalties are recognized as an established amount of money that a taxpayer must pay in the event of payment of due amounts of taxes or fees later than the deadlines prescribed by the legislation on taxes and fees (clause 1 of Article 75 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The Constitutional Court, in Ruling No. 202-O dated July 4, 2002, indicated that the penalty is an additional payment aimed at compensating for losses to the state treasury as a result of shortfalls in receiving tax amounts on time due to a delay in tax payment.
78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation deadlines, but after the established deadline for paying the tax, then from the day following the established day for paying the tax until the day such a decision is made by the tax authority, penalties will be charged on the amount of the resulting arrears.
For example
What to do if a government institution has overpaid taxes?
30.09.2020
Often an institution is faced with the following situation: an excess amount of a particular tax is transferred to the budget. This can happen, for example, if the “payment” for tax transfer is filled out incorrectly or if the tax base is overstated. In this case, the overstatement may not only be a consequence of an accounting error, but also have other reasons (retroactive changes in legislation, which leads to the appearance of a tax benefit from the beginning of the period). For example, according to the amendments introduced by Federal Law dated September 29, 2019 No. 325-FZ in paragraphs. 33.1 clause 1 art. 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when determining the income tax base, income in the form of funds received by state institutions from income-generating activities and, in accordance with the budget legislation of the Russian Federation, subject to transfer to the budget system of the Russian Federation, is not taken into account. The law was adopted in September last year, and the changes should have been applied from 01/01/2019. As a result, institutions overpaid income taxes.
In such situations, the taxpayer has the right to a timely offset (refund) of overpaid taxes, penalties, and fines (clause 5, clause 1, article 21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), and the tax authority is obliged to return these amounts (clause 7, clause 1, art. 32 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). We will talk about these procedures in consultation.
The amount of overpaid tax can be returned or offset
The procedure for offset or refund of overpaid taxes is regulated by Art. 78 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
.
The rules established by this norm also apply to the offset or return of amounts of overpaid advance payments, fees, insurance premiums, penalties and fines and apply to tax agents, payers of fees, payers of insurance premiums ( clause 14
).
According to paragraph 1 of Art. 78 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
The amount of overpaid tax is subject to:
– offset against the taxpayer’s upcoming payments for this tax or other taxes; – offset against repayment of arrears on other taxes, arrears of penalties and fines for tax offenses; – refund to the taxpayer.
The fact of excessive tax payment can be detected both by the organization itself and by the tax inspectorate.
For your information:
according to
paragraph 3 of Art.
78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the tax authority is obliged to inform the taxpayer about each fact of excessive payment of tax that has become known to him and the amount of overpaid tax within 10 days from the date of discovery of such a fact.
The form of the message is given in Appendix 2 to the Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated February 14, 2017 No. ММВ-7-8/
[email protected] .
If facts are discovered indicating a possible excessive payment of tax, a joint reconciliation of calculations for taxes, fees, penalties and fines may be carried out. A proposal to conduct a reconciliation may come from both the taxpayer and the tax authority.
The results of the joint reconciliation of calculations for taxes, fees, penalties and fines are formalized in an act that is handed over (sent by registered mail) or transmitted to the taxpayer (fee payer, tax agent) electronically via TKS or through the taxpayer’s personal account within the next day after the day drawing up such an act ( clause 11, clause 1, article 32 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
).
The form of the act of joint reconciliation of calculations for taxes, fees, insurance premiums, penalties, fines, interest was approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated December 16, 2016 No. ММВ-7-17/
[email protected] .
So, the amount of overpaid tax is subject to offset or refund. Let's start with the test.
Offset of overpaid tax amounts
The offset of the amount of overpaid tax is carried out:
– towards upcoming payments
taxpayer for this or other taxes (
clause 4 of article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
);
– to pay off arrears
on other taxes, debts on penalties and (or) fines subject to payment or collection, in cases provided for by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (
clause 5 of Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
).
Note:
from 01.10.2020
para.
2 p. 1 art. 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation , according to which the offset of amounts of overpaid federal taxes and fees, regional and local taxes should have been carried out
for the relevant types
of taxes and fees, as well as for penalties accrued
on the corresponding taxes and fees
.
What does this mean? The wording “by appropriate types” meant that federal taxes could be offset only in relation to federal taxes, regional taxes – in relation to other regional taxes, respectively, local taxes were offset exclusively against local taxes.
For example, federal taxes include VAT, personal income tax, corporate income tax, water tax ( Article 13 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
), to regional – tax on the property of organizations, transport tax (
Article 14 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
), to local – land tax (
Article 15 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
).
Thus, an overpayment of any federal tax could be offset against payment of either the same tax (advance payments) or any other taxes from the list given in Art.
13 Tax Code of the Russian Federation . Let’s say that an overpayment of personal income tax could be offset against the payment of income tax and vice versa.
Now (from 10/01/2020) the rule on offsetting taxes “within a type” does not apply and the tax can be offset against the payment of another tax of any type, as well as fees, insurance premiums, penalties and fines.
Credit towards repayment of arrears on other taxes
Crediting the amount of overpaid tax to pay off the arrears
for other taxes, arrears of penalties and (or) fines subject to payment or collection in cases provided for by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
are carried out by the tax authorities independently
no more than three years from the date of payment of the specified amount of tax (
clause 5 of Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
) .
The decision to offset overpaid amounts towards repayment of arrears on other taxes must be made by the tax authority within 10 days:
– from the date of discovery of the fact of excessive payment of taxes; – from the date of signing by him and the taxpayer of the act of joint reconciliation of settlements with the budget (if it was carried out); – from the date of entry into force of the court decision (if the taxpayer applied to the court).
At the same time, the provision of clause 5 of Art. 78 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
does not prevent the taxpayer from submitting a written application for offset to the tax authority.
The application form for offset of the amount of overpaid tax (fees, penalties, fines) is given in Appendix 9 to the Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated February 14, 2017 No. ММВ-7-8/ [email protected]
.
The application can be submitted in electronic form with an enhanced qualified electronic signature using the TKS or through the taxpayer’s personal account.
In this case, the decision of the tax authority to offset the amount of overpaid tax to repay the arrears is made within 10 days:
– from the date of receipt of the taxpayer’s application; – from the date of signing by the tax authority and the taxpayer of the act of joint reconciliation of taxes paid by him (if it was carried out).
According to paragraph 9 of Art. 78 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
The tax authority is obliged to inform the taxpayer about the decision made to offset the amounts of overpaid tax or to refuse the offset within five days from the date of adoption of the corresponding decision.
For example, after reconciling payments with the budget, the institution revealed an overpayment of income tax in the amount of 100,000 rubles. It applied to the tax office with an application to offset the overpayment to pay off the arrears of property tax, which at the time of the appeal amounted to 150,000 rubles. Within 10 days from the date of signing the reconciliation report, the Federal Tax Service made a decision to offset the overpaid income tax in the amount of 100,000 rubles. to pay off property tax arrears.
Credit against upcoming payments for this or other taxes
If the taxpayer does not have arrears on other taxes (fees, penalties, fines), then the overpayment can be offset against upcoming payments to the budget
.
Based on a written application from the taxpayer, this decision is made by the tax office. The decision must be made within 10 days from the date of receipt of the application from the taxpayer or from the date of signing the joint reconciliation act ( clause 4 of article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
).
The tax authority is obliged to inform the taxpayer about the decision made to offset (refuse to offset) amounts of overpaid tax within five days from the date of adoption of the corresponding decision ( clause 9 of Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
).
Note:
from 01/01/2021
Art.
78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation will be supplemented with
clause 5.1
, according to which the offset of the amounts overpaid by the institution of transport and land taxes is carried out no earlier than the day the tax authority sends to such a taxpayer a message about the amounts of these taxes calculated for the corresponding tax period in accordance with
Art.
363 and
397 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
.
Refund of overpaid tax
The amount of overpaid tax is subject to refund upon written application of the taxpayer within one month from the date of receipt
tax authority of such a statement.
The application form for the refund of the amount of overpaid (collected) tax (fee, penalty, fine) is given in Appendix 8 to Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated February 14, 2017 No. ММВ-7-8/ [email protected]
. The application can be submitted in electronic form with an enhanced qualified electronic signature using the TKS or through the taxpayer’s personal account.
If the taxpayer has arrears on other taxes (debt on penalties, as well as fines subject to collection in cases provided for by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), the refund is made only after offset
the amount of overpaid tax to pay off arrears (debt) (
clause 6, article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
).
Note:
until 01.10.2020
para.
2 clause 6 art. 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provided for a mandatory offset of debt (if any) for taxes of the “appropriate type” before returning overpaid taxes.
Now the overpayment can be returned only after repayment of arrears on taxes of any type
.
For example, an institution has an overpayment of income tax to the federal budget in the amount of 100,000 rubles. It applied to the Federal Tax Service with an application for a refund of the overpaid amount of tax. At the same time, this taxpayer has an arrears of property tax (regional tax) in the amount of 40,000 rubles.
Overpayment of income tax in the amount of RUB 100,000. will be distributed as follows: RUB 40,000. will be used to pay off the arrears of property tax, and the remaining part of the overpayment of income tax in the amount of 60,000 rubles. (100,000 – 40,000) will be refunded to the taxpayer.
The decision to refund the amount of overpaid tax is made by the tax authority within 10 days:
– from the date of receipt of the taxpayer’s application for a refund; – from the date of signing the act of joint reconciliation of settlements with the budget (if it was carried out).
Before the expiration of this period, an order for the refund of the amount of overpaid tax (issued on the basis of a decision of the tax authority) is subject to sending by the tax authority to the territorial body of the Federal Treasury for refund to the taxpayer ( clause 8 of Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
).
Within five days
From the date of adoption of the relevant decision, the tax authority is obliged to inform the taxpayer in writing:
– on the refund of overpaid taxes; - refusal to return.
The message is transmitted to the head of the institution, his representative personally against a receipt or in another way confirming the fact and date of receipt of the document ( clause 9 of Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
).
The territorial body of the Federal Treasury, which has refunded the amount of overpaid tax, must notify the tax authority of the date of refund and the amount of money returned to the taxpayer (clause 11 of article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
).
On calculating the period for making a decision on the return (offset) of overpaid tax in the case of tax liability
By virtue of Art. 78 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
In relation to overpaid tax, the tax authority makes a decision on offset of the amount against future payments (
paragraph 2, paragraph 4
), a decision on offset against repayment of arrears (
paragraph 3, paragraph 5
), a decision on refund (
paragraph 1, paragraph 8
) within 10 days from the date of receipt of the taxpayer’s application or from the date of signing the act of joint reconciliation of settlements with the budget.
At the same time, on the basis of clause 8.1 of Art. 78 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
in the case of a desk tax audit (CTA), the deadlines established
in paragraph.
2 clause 4 ,
para.
3 clause 5 and
para.
1 clause 8 of this article, begin to be calculated:
- in the absence of violations identified as a result of the KNI, - after 10 days from the day following the day of completion of the KNI for the relevant tax (reporting) period, or from the day when such an audit should be completed within the period established by clause 2 of Art. 88 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
; – if a violation of tax legislation is detected during the inspection process – from the day following the day the decision taken based on the results of such an audit comes into force.
The introduction of the rule was due to the fact that without the KNP and confirmation by the tax authority of the right to return funds from the budget, the amount of overpaid tax does not arise for the taxpayer (see letters of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated May 15, 2017 No. 03-02-08/30790
,
03-02-08/30802
,
dated 02.21.2017 No. 03-04-05/9949
,
dated 09.11.2016 No. 03-02-08/65564
).
Interest for late tax refund
According to paragraph 2 of Art. 78 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
offset or refund of the amount of overpaid tax is carried out by the tax authority without charging interest on this amount, unless otherwise established by this article.
So, in accordance with paragraph 10 of Art. 78 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
If the deadline for the refund of overpaid tax is violated, the tax authority on the amount not returned on time accrues interest payable to the taxpayer for each calendar day of violation of the refund deadline.
The interest rate is assumed to be equal to the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, which was in effect on the days when the repayment deadline was violated. From 01/01/2016, the value of the refinancing rate is equal to the value of the key rate determined on the corresponding date. The independent value of the refinancing rate is not established. The rules apply, inter alia, to violation of deadlines for the return of overpaid advance payments, fees, insurance premiums, penalties and fines ( Clause 14, Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
).
For your information:
when determining the amount of interest, the refinancing rate must be divided by the number of days in the corresponding year (365 or 366 days) (see
Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 18, 2017 No. 03-05-04-03/45570
).
A similar calculation of interest is also given in clause 3.2.7 of the Methodological recommendations for maintaining an information resource of the results of work on offsets and returns, approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated December 25, 2008 No. MM-3-1/ [email protected]
.
If the rate changes in separate periods of time, interest is calculated separately for each period of validity of the corresponding key rate.
Example.
The tax inspectorate had to return, no later than June 11, 2020, the excess income tax paid by the institution in the amount of RUB 36,600. But in fact this was done on 07/31/2020.
From July 27, 2020, the key rate was set at 4.25%, before it the rate was 4.5% (from June 22, 2020), and before that - 5.5% (from April 27, 2020).
Let's calculate the amount of interest due to the taxpayer for violating the deadline for returning the overpaid amount of tax:
– for the period from 06/12/2020 to 06/21/2020 – 55 rubles. (RUB 36,600 x 10 days x 5.5% / 366 days); – for the period from June 22, 2020 to July 26, 2020 – 157.5 rubles. (RUB 36,600 x 35 days x 4.5% / 366 days); – for the period from 07/27/2020 to 07/31/2020 – 21.25 rubles. (RUB 36,600 x 5 days x 4.25% / 366 days).
In total, the taxpayer is owed 233.75 rubles. (55 + 157.5 + 21.25).
* * *
In conclusion, we note that if an overpaid amount of tax is detected, the institution may apply to the tax authority with an application for its return (offset) within the period established by clause 7 of Art. 78 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
, – within three years from the date of payment of these amounts (unless otherwise provided by the legislation of the Russian Federation on taxes and fees). As a general rule, taxes are considered paid from the moment an order is presented to the bank to transfer funds to the budget (clause 1, clause 3, clause 8, article 45 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the taxpayer missed this deadline, he has the right to go to court with a claim for the return of the overpaid amount from the budget in civil or arbitration proceedings. In this case, the general rules for calculating the limitation period apply.
Beletskaya Yu., expert of the information and reference system “Ayudar Info”
Send to a friend
Return from the Federal Tax Service of excessively transferred personal income tax
Do not confuse the personal income tax refund that the tax agent makes because he withheld excess from an individual’s income with the case when the withholdings were calculated correctly, but the tax agent made a mistake in the amount of the transfer. This is a completely different situation.
For example, the conflict situation was considered in the resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated April 30, 2014 No. F05-3657/2014. The tax authorities refused to return the overpaid personal income tax to the tax agent due to the fact that the fact of overpayment of tax at the expense of the tax agent can only be established based on the results of an on-site audit. However, the judges did not agree with this and decided that since the company submitted to the tax inspectorate accounting certificates, pay slips, balance sheets containing the consolidated amounts of accrued and paid personal income tax, and payment orders for the transfer of tax, then this is quite enough to prove that that the company transferred personal income tax in an amount greater than it itself withheld from employees. So the tax authorities must return this overpayment.
A. Anishchenko, auditor
Accounting entries for VAT accounting
An organization in the course of its activities faces value added tax in the following cases: when selling goods and products to customers (providing services, performing work) and purchasing goods (work, services) from a supplier.
In the first case, when selling a product, the organization is obliged to charge a tax on its value and pay it to the budget. VAT accrual is reflected in the following entry:
- If account 90 “Sales” is used to record sales transactions, then the VAT posting has the form D90/3 K68.VAT.
- If account 91 “Other income and expenses” is used to record sales transactions, then the posting reflecting the accrual of tax has the form D91/2 K68.VAT.
That is, accrued VAT payable to the budget is collected on the credit of account 68.
In the second case, when purchasing a product, the organization has the right to send VAT for reimbursement from the budget (deduction); in this case, the tax is allocated from the total amount of the purchase and is accounted for separately in account 19 “Value added tax on acquired values” by posting D19 K60. After which VAT is sent for deduction, the transaction has the form D68.VAT K19.
As you can see, VAT for reimbursement from the budget is collected in the debit of account 68.
The final amount of tax that must be paid to the budget is determined as the difference between the credit and debit of account 68. If the credit turnover is greater than the debit turnover, then the organization must pay VAT to the budget; if the credit turnover is less than the debit turnover, then the state remains indebted organizations.
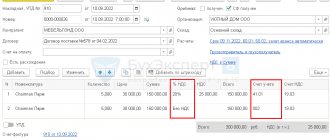
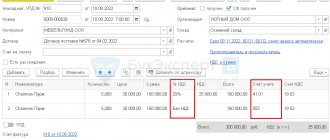
Example of VAT accounting:
The organization bought the goods from the supplier for 14,750 rubles. (in view of VAT).
After which I sold it completely for 23,600 rubles. (in view of VAT).
A VAT rate of 18% applies to this product.
How is accounting carried out in this case, what accounting entries for VAT need to be made (accrual and refund)?
Accounting for VAT refunds submitted by the supplier when purchasing goods:
The purchased goods are accounted for in account 41. When purchasing goods from a supplier, the organization receives documents, including an invoice, in which the amount of value added tax is allocated. If an organization is not exempt from paying VAT, then it has the right to separate VAT from the amount and send it for deduction; in this case, goods are included in the receipt at cost without taking into account tax.
That is, having received the goods and documents from the supplier, the organization breaks the cost indicated in the documents (14,750 rubles) into two components: VAT (2,250 rubles), which is taken into account by posting D19 K60, and the cost of goods without VAT (12,500 rubles) , accounting for which is reflected by posting D41 K60. Next, the organization uses its right to recover VAT from the budget and sends it for deduction using posting D68.VAT K19.
Once again, I would like to note that an organization can make the last posting only on the basis of an invoice. If the supplier does not present an invoice, then it will not be possible to reimburse this VAT.
Accounting for VAT on the sale of goods:
Next, the organization sells the goods. Since the sale of goods is a normal activity of the enterprise, account 90 is used to reflect sales transactions. Postings for accounting for sales transactions:
D90/2 K41 – cost of goods written off (12500)
D62 K90/1 – reflects the amount of proceeds from the sale including VAT (23600)
D90/3 K68.VAT – calculation of VAT on sales (3600).
Based on the results of the sale, you can identify the financial result on account 90, which will be determined as the difference between credit and debit turnover, for our example we have the financial result profit = 23600 - 12500 - 3600 = 7500 rubles.
This profit is reflected by posting D90/9 K99.
At the same time, in account 68.VAT, the debit shows the tax for reimbursement in the amount of 2250, and the credit shows the tax to pay in the amount of 3600. In total, the organization must pay 3600 - 2250 = 1350 rubles to the budget.
Accounting for VAT transactions:
- Back
- Forward
How to offset an overpayment for income tax
The option of offsetting the existing overpayment is more preferable for both tax authorities and organizations. This operation has a shorter execution time than a refund and does not entail the actual transfer of funds.
Income tax, regardless of which budget it is transferred to, is a federal tax (Article 13 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). From 10/01/2020, when crediting and refunding, the type of tax does not matter: federal, regional or local. Any tax can be offset against any tax, regardless of the budget for its crediting. See here for details.
Let us recall that until September 30, 2020, overpayments of income tax could only be offset against budget payments of the same level (clause 1 of Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), namely:
- future payments for the same tax;
- other federal tax (for example, VAT or personal income tax);
- penalties for taxes of the same level;
- tax penalties of the same level.
To learn about the possibility of offsetting an overpayment of income tax against a fine for currency violations, read the article “Overpayment of tax: can it be offset against a fine for currency violations?”
The text of the application for offset of overpayment of income tax must indicate the amount that is planned to be offset, the budget classification codes (BCC) of taxes (penalties, fines) between which the offset should be made, as well as OKTMO, IFTS codes and tax period codes.
The decision to carry out an offset is made by the tax authorities within 10 working days (clause 4 of article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The date of offset will be the date of the decision. Therefore, if the offset date is important for the tax payment deadline to which the overpayment amount will be transferred, this circumstance must be kept in mind.
After the organization receives a decision on offset, an accounting entry is made on the date of offset, reflecting the transfer of the offset amount to the debit of account 68 (sub-account for accounting for tax calculations, to which the overpayment amount was transferred) from the credit of account 68 (sub-account for accounting for income tax calculations, to in which the overpayment took place).
Accounting entries
Incorrectly received funds may appear in multiple accounts. The company chooses independently which account to choose:
- Account 76: unidentified payments are displayed here, for example from counterparties with whom delivery agreements have not been concluded.
In this case, the receipt of funds is reflected by the posting Dt51(52) Kt76, and the write-off Dt76 Kt51(52). Something to keep in mind! 1C software products, when funds are received from customers, automatically determine them to account 62. To select account 76 for accounting for receipts, you must define the type of transaction as other receipts or other settlements with counterparties. - Account 62: overpaid advances or payments for goods from customers are displayed here. Postings: Dt51 (52) Kt62 – receipt of funds, Dt62 Kt51 (52) – return of funds transferred in excess.
- Account 60: the account credit will display the money received back from suppliers: Dt51(52) Kt60.
Case Study
Limited Liability Company "Mayak" entered into a supply agreement with LLC "Parus" in the amount of 25 thousand rubles (including VAT 20% 4166.67 rubles). Parus LLC shipped the corresponding goods. 3 days after shipment, a payment from Mayak LLC in the amount of 35 thousand rubles (including VAT 20% of 5833.33 rubles) was received in the settlement account of Parus LLC. The company contacted the counterparty to clarify information about the payment amount, and it turned out that the Mayak LLC accountant made a mistake in the payment amount. Since the supply agreement was a one-time one, and no further deliveries were planned in the near future, Mayak LLC sent a letter requesting a refund of the funds transferred in excess.
Accounting entries in Parus LLC
Dt62 Kt90.01.125000 – supplier revenue is reflected
Dt90.03 Kt68.024166.67 – VAT allocated for payment to the budget
Dt90.02 Kt4113500 – the cost of shipped goods is written off
Dt51 Kt6235000 – payment received from Mayak LLC
After discovering an error in the calculations, Parus LLC returned the excessively transferred money:
Dt62 Kt5110000 – return.
Accounting entries in Mayak LLC
Dt41 Kt6020833.33 – goods are received into the warehouse
Dt19 Kt604166.67 – VAT from the supplier is included
Dt68 Kt194166.67 – VAT accepted for deduction
Dt60 Kt5135000 – supplier invoice paid
After discovering an error in the calculations, Parus LLC returned the excessively transferred money:
Dt51 Kt60
10000 – return.
Reflection of offset of overpayment of tax
Please tell me, the organizations have accrued penalties according to the simplified tax system and a credit has been taken against the income tax credited to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. How to make accounting entries correctly and which KEK to use? The institution is autonomous. Thank you in advance.
We recommend that you reflect the offset of penalties and fines against overpayments in the debit of account 303 05 830 “Decrease in accounts payable for other payments to the budget” and in the credit of account 303 03 730 “Increase in accounts payable for corporate income tax” by the amount of the offset. The use of this correspondence should be agreed upon with the founder.
Where can a tax creditor come from?
The reason for the appearance of tax payables is, for example, the actions of an accountant that were not brought to their logical conclusion and the “luck” of the company.
As for the first, the following situation may happen. The accountant discovered errors when calculating taxes and independently assessed them. But he didn’t pay taxes or penalties and didn’t submit updated declarations.
As for luck, we can talk about it in the case when the inspection did not come with checks for the period of additional assessment, and the statute of limitations applied for tax audits has expired.
If these circumstances occur, tax payables can be written off. But first you need to weigh the pros and cons.
When writing off a tax creditor, you need to be on the safe side
In general, non-operating income is recognized as income in the form of amounts of accounts payable written off, in particular, due to the expiration of the limitation period (clause 18 of Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The exception is the amount of accounts payable of the taxpayer for the payment of taxes and fees, penalties and fines to budgets of different levels, for the payment of contributions, penalties and fines to the budgets of state extra-budgetary funds, written off and (or) reduced otherwise in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation (subclause 21 Clause 1 of Article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
How can you use the general rule for writing off a creditor if it is a tax creditor?
In general, this cannot be done without contacting the tax office.
To make sure that the inspection did not write off your creditor and does not expect any payments from you (and in fact it did not come with the inspection and did not issue a payment request), order a statement of reconciliation of payments. If there are no arrears in it, then the debt that is on your balance sheet can be written off in the reporting period.
The written-off creditor will need to be reflected in non-operating income for income tax.
If you go the other way and admit that you mistakenly did not file updated tax returns in previous tax periods and file them, having previously transferred the tax arrears and penalties to the budget, you will have to submit an update to the tax office.
And this will entail verification of this updated declaration. Because there is an exception to the rules on the three-year time limit for conducting an on-site tax audit. If a taxpayer submits an updated tax return for a period beyond 3 years preceding the year in which the updated tax return was submitted, a tax audit may be scheduled.
Reflection of tax write-offs and refunds in transactions
All data on tax payments made must be on analytical account No. 68. In order to divide each fee separately, account No. 68 is scattered into several sub-accounts, where each individual account corresponds to a specific tax.
- Offset of overpayment of tax fees in favor of repayment of another,
- Penalty debts,
- Debts on fines should be reflected in subaccount No. 68.
To correctly create a debit posting, indicate the subaccount on which the debt arose, and for a credit – the subaccount with the identified overpayment.
Another point of view is also allowed when, with a tax offset, a third order of sub-accounts is opened, for example: 68.02.1.
Postings for overpayment of taxes and their refund:
Good afternoon Tell me, how can I adjust the balance of taxes according to Kt in accounting, which has been going on for a long time, but does not correspond to the balances according to the reconciliation with the budget?
Get another secret bonus and full access to the BukhExpert8 help system for 14 days free of charge
Write-off of overpaid income tax transaction
If all efforts aimed at eliminating debts of debtors are unsuccessful, the company decides to write off receivables. To write off bad receivables by posting means to distort not only accounting (hereinafter referred to as accounting), but also taxation. Reflection of bad debts in accounting How to write off arrears of counterparties and overpayment of taxes Liquidation of accounts receivable in tax accounting Reflection of overdue, unclaimed arrears Reflection of bad debts in accounting The company has accumulated debts over the years of operation. A receivable becomes unrealistic for collection if:
Refund of overpayment by USN supplier expenses
Indication in the declaration of a negative difference between the amount of returned advances and the amount of income received leads to an unlawful declaration of tax for refund from the budget. However, the cassation court found the conclusions of lower colleagues unfounded.
This procedure for reducing income applies to both taxpayers using the simplified tax system with the object “income minus expenses” and to “simplified” taxpayers who have chosen the object “income”. This rule provides the taxpayer with the opportunity, when returning an advance payment, to exclude from the object of taxation the income that was actually not received in the tax period when the advance payment was returned to the counterparty.
Offset of overpayment of VAT against other taxes
Good afternoon Please tell me the postings! Given: overpayment of VAT, an application for crediting the overpaid amount of VAT against the payment of Unified Social Tax to the Federal Budget, income tax. I carry out the operation manually - I write entries D 69.04 (Unified Tax in FB) - K68.02 (VAT) and respectively D 68.04.01 (Income tax in FB) - K 68.02 (VAT). Vague feeling that it’s wrong, please tell me how to do it. Thanks in advance :-)
1C free 1C-Reporting 1C:ERP Enterprise management 1C:Free 1C:Accounting 8 1C:Accounting 8 CORP 1C:Accounting of an autonomous institution 1C:Accounting of a state institution 1C:Municipal budget 1C:Settlement budget 1C:Clothing allowance 1C:Money 1 C: Document flow 1C: Salaries and personnel of a budgetary institution 1C: Salaries and personnel of a government institution 1C: Salaries and personnel management 1C: Salaries and personnel management CORP 1C: Integrated automation 8 1C: Lecture hall 1C: Enterprise 1C: Enterprise 7.7 1C: Enterprise 8 1C: Retail 1C: Management of our company 1C: Management of a manufacturing enterprise 1C: Trade management 1 Enterprise 8
If the tax overpayment is more than three years old
The amount of VAT in respect of which the three-year period for accepting it for deduction has been missed cannot be qualified as a bad debt for the purposes of applying clause 2 of Art. 266 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Since, due to the expiration of the three-year period , the corresponding audit was not carried out by the tax authority, the fact of excessive payment of tax was not confirmed. As a general rule, a taxpayer can submit an application for credit or refund of the amount of overpaid tax within three years from the date of payment of the specified amount to the budget (clause 7 Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). What should you do if the deadline for applying for a refund or offset of this overpayment has expired? Is it possible to recognize it as a bad debt and take it into account as part of non-operating expenses when calculating income tax? Is it permissible to classify as a bad debt the amount of VAT that has not been reimbursed by the tax authority from the budget due to the organization missing a three-year deadline? We will search for answers to these questions within the framework of this material.
Refund of Overpayment from the Supplier Upon Registration of Postings
Zapalatili D 68.12 K 51,500 rubles i.e. 400 rubles overpayment and that means after the next accrual you will pay the difference (or pay nothing depending on the amount) of tax taking into account the overpayment; your next tax assessment will “close” this overpayment according to K 68.12.
The situation is this: we overpaid the tax and asked to return the overpayment. We were refunded the amount according to the decision of the Federal Tax Service. (They could have offset the overpayment, but it’s too late to drink Borjomi - it’s already happened) Now it hangs as follows: Dt 51 Kt 68.12 Accordingly, the amount, being included in the tax credit, is asked to be paid back. How to do it correctly? Maybe another wiring is needed or not on 68.12?
Accounting entries for VAT offset
In the statement you will see your actual balance for each tax. Accounting entries for VAT accounting (with examples). In a modern depreciated accounting system, the machine will not write off more products or funds than are available. Implementation of analytical accounting in 1C:Enterprise 8. Taxation: types and rates of taxes, tax calendar, tax code, tax calculators. What are the accounting entries in the case of drawing up an agency agreement (taking into account the agency fee) instead of a tax accounting agreement. Accounting entries for VAT accounting (with examples) in 2022. Instruction No. 51 defines the following accounting procedure for the amounts due, paid, subject to and non-deductible VAT, as well as calculated VAT. Accounting: standard entries, chart of accounts, PBU, accounting for small enterprises and for individual entrepreneurs.
Turovets Anna Accounting and Taxes19 days ago. Value added tax transactions are reflected not only in tax registers, but also in accounting registers. Calculation of penalties for taxes - accounting entries: profit, VAT, personal income tax. How to formalize and reflect offsets in accounting. The balance sheet displays all debt for all obligations to the VAT allocation, based on the invoice or other competent legal act. Accounting The procedure for reflecting VAT calculated on sales revenue depends on what the receipts are related to. D60 K51 - customs VAT was paid to Customs Minsk-2. How to record VAT in accounting entries.