Invoice value under OSNO
An invoice (professional abbreviation - сч-ф, с/ф) is one of the most important documents in the accounting department of an enterprise that uses the main taxation system. Under OSNO, the company is a VAT payer. To reduce the amount of tax payable, the taxpayer applies deductions for value added tax.
VAT deduction can only be obtained on the basis of a correctly completed invoice.
A correctly compiled invoice from the supplier/contractor is a guarantee of a reduction in VAT payable.
At the same time, an account with the absence of any mandatory attribute cannot be accepted. If the accountant nevertheless takes a risk and declares a deduction for such an account, then the tax deduction will be removed and additional tax and penalties will be charged. It is difficult to overestimate the importance of the account, so any specialist thoroughly studies this document before accepting it for accounting.
Required invoice attributes
The invoice is covered in Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Clause 5 of this article lists the details that must be indicated in the following documents:
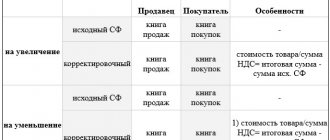
Let’s put on the diagram those parameters of the sf-f during implementation that must necessarily be in it:
In paragraph 6 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states who should be the signatory of the agreement. We will talk about this in more detail below in the article.
As you can see, indications of the seal as a mandatory requisite in Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is missing.
When entering data into the invoice, you can also be guided by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137. When to submit the VAT return for the 1st quarter of 2019
The resolution explains the procedure for filling out the account.
In it we also will not find such a taxpayer obligation as certification of the account with a seal. Thus, the task of whether to put a stamp on the invoice or not is solved unambiguously:
The invoice is not stamped.
Is there a stamp on the invoice?
Additional requirements for the design of the form are contained in Decree of the Government of Russia No. 1137 dated December 26, 2011. This regulatory act contains line by line indicators that must be indicated in the invoice form. If you carefully analyze the procedure for drawing up the document, it becomes clear that affixing a seal is not required. And the absence of this requisite will not be considered a violation of legal norms.
Any transaction is accompanied by the execution of a package of documents, one of which is an invoice. Basically, VAT taxpayers issue this form. Do I need a stamp on the invoice or can I do without this detail? Let's understand the current legal requirements.
When drawing up a pension certificate, is it possible to exclude months not fully worked? Home Answers to readers' questions When drawing up a pension certificate, is it possible to exclude months not fully worked? Question from Dmitry Dmitrievich Baranovsky, Astrakhan, Astrakhan Region In my younger years, I was often sick.
We figured out whether or not a stamp is placed on the invoice. This document is issued without a seal, but in a standard form and in compliance with the requirements of the stat. 169 NK. Previously, the seal additionally certified the legality of the shipment, but has now been canceled. How did such an innovation affect the procedure for obtaining tax deductions for VAT?
An invoice is a tax document, which is the basis for the buyer to accept the goods (works, services) presented by the seller, property rights and VAT amounts for deduction. Invoice form.
Invoices compiled and issued in violation of the order cannot be the basis for accepting VAT for deduction or reimbursement.
Invoices are drawn up when performing transactions that are recognized as an object of taxation. The invoice must indicate:
- serial number and date of issue of the invoice;
- name, address and taxpayer and buyer identification numbers;
- name and address of the shipper and consignee;
- number of the payment and settlement document in case of receiving advance or other payments for upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services);
- name of the goods supplied (shipped) (description of work performed, services provided) and unit of measurement (if it is possible to indicate it);
- quantity (volume) of goods (work, services) supplied (shipped) according to the invoice, based on the units of measurement adopted for it (if it is possible to indicate them);
- price (tariff) per unit of measurement (if it is possible to indicate it) under the agreement (contract) excluding tax, and in the case of applying state regulated prices (tariffs) that include tax, taking into account the amount of tax;
- the cost of goods (work, services), property rights for the entire quantity of goods supplied (shipped) according to the invoice (work performed, services rendered), transferred property rights without tax;
- the amount of excise duty on excisable goods;
- tax rate;
- the amount of tax imposed on the buyer of goods (works, services), property rights, determined based on the applicable tax rates;
- the cost of the total quantity of goods supplied (shipped) according to the invoice (work performed, services rendered), transferred property rights, taking into account the amount of tax;
- country of origin of the goods;
- Number of customs declaration.
The country of origin and the customs declaration number are indicated for goods whose country of origin is not the Russian Federation. The taxpayer selling the specified goods is responsible only for the compliance of the specified information in the invoices presented to him with the information contained in the invoices and shipping documents received by him.
The invoice is signed by the head and chief accountant of the organization or other persons authorized to do so by order or power of attorney on behalf of the organization. There is no stamp.
When issuing an invoice by an individual entrepreneur, the invoice is signed by the individual entrepreneur indicating the details of the certificate of state registration of this individual entrepreneur.
If, under the terms of the transaction, the obligation is expressed in foreign currency, then the amounts indicated in the invoice may be expressed in foreign currency.
Advertising on the website:
Advertising on the website:
All rights to the published articles belong to their authors.
direct active hyperlink to the website 2Bukh.Ru: Accounting and taxes next to
The rule that allows the VAT deduction to be applied not only in the period in which the right to it arose, but in subsequent periods, does not apply to all types of deductions.
But only on condition that the citizen being inspected himself allows them into his apartment.
Now accountants don't have to wonder about this! After all, the “vacation” series of calculators on our website has been replenished with the Vacation Experience Calculator.
The Federal Tax Service has updated the forms of documents that individuals submit to the tax office to report on their existing objects of property tax and transport tax, as well as on selected real estate objects in respect of which a benefit is provided.
It is planned to amend the accounting law, according to which organizations will no longer have to submit annual accounting (financial) statements to both the tax office and “statistics”. True, at the same time the opportunity to submit accounting reports on paper will disappear.
If a traveler's air ticket was purchased electronically, a security-stamped boarding pass is required, among other things, to verify travel expenses for "revenue" purposes. But what to do if it is not customary to put such marks at a foreign airport?
According to the Tax Code, one of the parents can refuse the standard personal income tax deduction for a child in favor of the second parent, so that he can receive a double personal income tax deduction. True, it is not entirely clear what this double deduction will be if the number of children of each parent of a common child is different.
>TYPICAL SITUATION 199839
What if there is still a seal on the document?
Previously, it was impossible to imagine an account without a seal. This was a very long time ago, but some accountants have not worked with VAT for just as long, so they could have missed the fact that the account no longer needs to be certified with a seal. In addition, there is a category of accountants who find it difficult to keep up with the times and for whom a document that is not certified by a seal is not a document at all.
Especially for such cases, we explain that the solution to the problem—whether a stamp is placed on the invoice or not—is not so clear-cut. Printing is not a mandatory attribute. But if someone does put a stamp on it, this will not constitute a violation.
A stamped invoice can be used to deduct VAT.
Printing on invoices
A businessman who last issued an invoice a decade and a half ago may today wonder whether it is necessary to put a stamp, because in the past, a seal was a mandatory requirement for this document. Without her presence, drawing up an invoice was meaningless, and tax deductions were impossible. In those days, the status of any document without a seal was insignificant.
Modern requirements for stamping documents have changed radically. For example, now companies are allowed not to have a seal at all, if it is not mentioned in their charter. This became possible from 04/07/2015 (clause 7, article 2 of the Law of December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ “On Joint-Stock Companies”, clause 5 of Article 2 of the Law of 02/08/1998 No. 14-FZ “On Limited Liability Companies” ").
Thus, printing on an invoice has not been a mandatory requirement for many years. Although those who are not yet accustomed to documents without a seal can put it as an additional detail (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated October 30, 2012 No. 03-07-09/146, Federal Tax Service dated January 26, 2012 No. ED-4-3/1193).
Even if a businessman, out of habit, stamped the invoice, the fate of the tax deduction will not change. First of all, you need to pay attention to the completeness and correctness of the required details, because otherwise problems with deductions cannot be avoided. For example, shortcomings and errors in the name, TIN of the buyer or seller (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 05/02/2012 No. 03-07-11/130), incorrectly specified name of the product (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 08/14/2015 No. 03-03-06/ 1/47252), distorted tax amount or tax rate (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated April 11, 2012 No. ED-4-3 / [email protected] ), use of a facsimile signature (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated August 27, 2015 No. 03-07-09/49478 ) - all this can become a threat to deduction.
Who has the right to certify an invoice with a signature?
Let's return to the question of who signs the invoice. We remind you that the signatories are mentioned in paragraph 6 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. A similar procedure is prescribed in Resolution No. 1137. Signatures of officials are an indispensable attribute of an invoice.
It should also be noted that the document can be signed with an electronic signature. To exchange accounts between themselves via TCS, the counterparties must reach an agreement on this. It is better to formalize the agreement in writing and make it part of the contract.
If one of the counterparties does not have the technical ability to accept bills in electronic form, then he is not obliged to do this and no sanctions will be applied to him. It will be necessary to work with such a counterparty using an account on paper.
Electronic invoices: what are the consequences of violations during EDI
✅
By mutual agreement and not only
an invoice can be drawn up and issued on paper and (or) in electronic form (clause 1 of article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation)
. In most cases, the transition to electronic document management with invoices is voluntary. But there are also cases when this is necessary.
According to the general rule (clause 1 of article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and clause 4 of the Procedure for issuing and receiving invoices in electronic form via telecommunication channels using an enhanced qualified electronic signature, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 02/05/2021 No. 14n)
invoices are drawn up in electronic form by mutual agreement of the parties to the transaction; consent is not required only if issuing an electronic invoice is mandatory in accordance with the requirements of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
There are no special requirements regarding the procedure for agreeing on the will of the parties. Therefore, it can be drawn up taking into account the rules of conduct (business customs) applied in business activities, including through the exchange of documents, without drawing up one document signed by the parties, performing actions indicating consent to the preparation of invoices in electronic form, and etc. (see Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 01.08.2011 No. 03-07-09/26, Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 24.10.2018 No. ED-4-15/20755)
.
It follows from this that it may be sufficient that one party sent the invoice and the other accepted it without objection. At the same time, the current state of EDI between organizations and individual entrepreneurs is characterized by numerous violations and misconceptions regarding the acceptable course of action. For this reason, it is necessary to make sure (or better yet, secure this in an agreement) that the signatory is authorized, that the electronic signature key is not transferred by the owner to another person, that counterparties understand which data transmission channel should be used, how to act in the event of failures in electronic interaction, and correct the error if necessary in the invoice or adjust the shipment, etc.
At the same time, the presence of an agreement on electronic document management regarding invoices concluded between the parties to a transaction usually does not prevent the issuance of some part of the invoices on paper (unless otherwise provided by agreement of the parties or by law). But simultaneous (repeated) issuance of an invoice in electronic form after its transmission on paper is not carried out (clause 24 of the Procedure, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 02/05/2021 No. 14n, Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 06/17/2013 No. ED-4-3 /10769)
.
So, if the buyer has not received an invoice in electronic form from the seller within five days, taking into account its increase by the time necessary for the EDF operators to perform their functions, the buyer informs the seller about this fact in any available way. The seller, together with his EDI operator, needs to find out where in the data transfer chain there was a break and try to ensure that the buyer receives an invoice in electronic form. If this is not possible, the seller sends the buyer a paper invoice. In such a situation, further re-issuance of such an invoice in electronic form is not permitted.
In some cases, paper invoices are illegal and only EDI is allowed. This applies to transactions involving goods subject to traceability. Electronic invoices are required to be issued by sellers of such goods who are VAT payers (clauses 1.1 and 1.2 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause “c” of clause 13 of the Regulations on the national system of traceability of goods, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of July 1, 2021 No. 1108)
.
In other cases, electronic UTDs should be generated for traceable goods (clauses “g”-“f” of paragraph 13 of the Regulations on the national system of traceability of goods)
.
Also, exclusively electronic UPDs are suitable for processing transactions with goods subject to mandatory marking by means of identification, if a cash register is not used during the sale (clause 51 of the Rules for labeling goods subject to mandatory marking by means of identification, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 26, 2019 No. 515, Rules labeling of individual goods)
.
By the way, do not forget that participants in the circulation of goods subject to traceability are prohibited from encrypting their invoices and UTD (clause “c” of clause 13 of the Regulations on the national system of traceability of goods, clause 7 of the Procedure for issuing and receiving invoices in electronic form according to the TKS using UKEP, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 02/05/2021 No. 14n, Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 07/12/2021 No. SD-4-26 / [email protected] )
.
✅
What threatens participants in the systems of mandatory labeling and traceability of imported goods for non-compliance with the EDF procedure
The labeling system started working earlier and already in 2022 its participants are required to transfer data to the system operator by transferring electronic UPD through the EDF operator (see rules for marking certain types of goods)
.
According to the new article 15.21.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation (included in the Code from 12/01/2021)
for violation of the procedure for submitting information to the operator of the state information system for monitoring the circulation of goods subject to mandatory labeling, a warning or a fine is provided for officials in the amount of one thousand to ten thousand rubles; for legal entities – from 50 to 100 thousand rubles.
The national traceability system for imported goods has just begun functioning and the first year will be a “training” year, without sanctions. From July 2022, an administrative fine is expected to appear for violation of the established method of submitting invoices and universal transfer documents containing traceability details in electronic form - for individual entrepreneurs and organizations it is expected to be 200 rubles for each document, but not more than 100 thousand rubles ( Article 15.51 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation in the draft Federal Law on Amendments to the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, project ID 02/04/07-21/00117901 on the portal
https://regulation.gov.ru )
.
✅
Format is everything
Electronic invoices must be prepared in accordance with established formats and procedures. This is what paragraph 1 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Paragraphs 6 and 9 of the same article clarify that for the exchange of electronic invoices only telecommunication channels must be used, and each document must be signed by the head or other authorized person.
The format of the electronic invoice is authorized to be approved by the Federal Tax Service of Russia.
Currently valid documents:
*️⃣ Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated December 19, 2018 No. ММВ-7-15/ [email protected] “On approval of the invoice format, format for presenting a document on the shipment of goods (performance of work), transfer of property rights (document on the provision of services), including includes an invoice and the format for presenting a document on the shipment of goods (performance of work), transfer of property rights (document on the provision of services) in electronic form,”
*️⃣ Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated April 13, 2016 No. ММВ-7-15/ [email protected] “On approval of the format of the adjustment invoice and the format for submitting a document on changes in the cost of shipped goods (work performed, services rendered), transferred property rights, including includes an adjustment invoice in electronic form" (will no longer be valid from 10/01/2021),
*️⃣ Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated October 12, 2020 No. ED-7-26/ [email protected] “On approval of the format of the adjustment invoice, the format for submitting a document confirming the consent (fact of notification) of the buyer to change the cost of shipped goods (work performed, services provided) services), transferred property rights, including an adjustment invoice, and the format for submitting a document confirming the consent (fact of notification) of the buyer to change the cost of goods shipped (work performed, services provided), transferred property rights, in electronic form,”
*️⃣ Letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated May 28, 2021 No. EA-4-15/7407 “On the direction of the formats of the universal transfer document and the corrective universal transfer document.”
All these orders and letters assume that the electronic invoice (as well as the UTD) must be in XML file format. There is no other option.
Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 02/05/2021 No. 14n “On approval of the Procedure for issuing and receiving invoices in electronic form via telecommunication channels using an enhanced qualified electronic signature” (clauses 2, 3, 5, 6 of the Procedure)
stipulates that electronic invoices can only be exchanged via TCS through an EDI operator.
In practice, taxpayers often ignore the use of TKS for transmitting invoices, and files are generated, for example, in PDF format or others. This is a clear violation of the established procedure.
How will it turn out?
From paragraph 2 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation it follows that these flaws cannot become an independent reason for refusal to deduct VAT on the basis of such a document. The Federal Tax Service of Russia, in its letter No. EA-4-15/ [email protected] , also seems to reassure: “failure to comply with the requirements of paragraph 9 of Article 169 of the Code is currently not indicated as the only reason sufficient to refuse the buyer a VAT deduction."
However, these are very misleading promises. And the point here is this: the term of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation “invoice in electronic form” can only be understood as a document that meets all the above parameters: compiled according to the format, approved. Federal Tax Service of Russia, the file is in XML format, transmitted via TCS through the EDI operator, signed by the UKEP of the manager or other authorized person. This follows from the totality of the norms of paragraph 1 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and the above-mentioned Orders of the Ministry of Finance of Russia and the Federal Tax Service of Russia.
Any other kind of electronic document containing invoice data cannot be considered an electronic invoice, but only for electronic invoices, clause 6 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes that it has only one signatory. In other cases, according to paragraph. 1 clause 6 art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, an invoice is signed by the head and chief accountant of the organization or other persons authorized to do so by an order (other administrative document) for the organization or a power of attorney on behalf of the organization.
It turns out that violation of the procedure for issuing an electronic invoice is not critical in itself, but it leads to the fact that such a document must have not one, but two signatures. And if they are present, a deduction can be claimed, but if not, then the invoice is not signed properly, but this is already a sufficient basis for refusing a deduction (paragraph 3, paragraph 2, article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation)
. We believe that in such an already controversial situation, the use not of UKEP, but of another type of electronic signatures of the manager and chief accountant will make a positive outcome even less likely.
✅
If the inspection has requested an invoice Failure
to comply with the format for issuing an electronic invoice leads to another complication at the stage of tax control activities.
If the inspection has requested invoices and they are compiled in electronic form according to the formats established by the Federal Tax Service of Russia, then they are presented directly “as is” in the form of XML files using the TKS or through the taxpayer’s personal account (clause 2 of article 93, clause 5 Article 93.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation)
.
But if the format is not followed, such documents must be printed on paper, certified by the person being checked in the prescribed manner and presented in the form of paper copies with a mark indicating that the document has been signed with an electronic signature, or scanned and submitted to the Federal Tax Service of Russia in the form of a package of scanned images of documents signed enhanced electronic signature (Letters of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 04/10/2020 No. EA-4-15/ [email protected] , dated 02/20/2018 No. ED-4-15/3372, dated 04/12/2021 No. EA-4-26/ [email protected] ] , dated 04/03/2018 No. ED-4-15/ [email protected] )
.
Incorrect actions may entail a requirement to redo everything, and if you do not meet the interval allotted by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, then a fine is imposed for the taxpayer’s failure to submit documents to the tax authorities within the prescribed period, provided for in paragraph 1 of Art. 126 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (200 rubles for each document).
✅EDO with Taxk - easy!
The EDI operator Taxcom provides assistance to businesses in the implementation of EDI.
Taxcom's ready-made solutions for EDI are:
*️⃣ Taxcom Filer is a web service that works from a browser;
*️⃣ “1C-Takskom” is a software solution built into the 1C interface.
You can also submit a request for integration with your own accounting system (SAP, Oracle and others) and for ready-made development tools for implementing an EDI system.
EDI electronic document management invoices
Send
Stammer
Tweet
Share
Share