What is revenue from product sales?
Revenue from product sales represents cash income received by an organization from customers for products sold. The indicator expresses the monetary relations between producers and consumers of goods. Revenue from sales of products is determined based on the quantity of products sold and their cost. For tax purposes, it is recognized as income from sales.
Revenue is not profit; a separate line is allocated for it in the “Income Statement”. The head of the organization must ensure the uninterrupted flow of revenue, since without this the business simply will not be able to function.
The following factors influence the amount of revenue from product sales:
- internal (production volume, range of manufactured goods, their quality and competitiveness, level of prices applied, cost, compliance with contractual terms, etc.);
- external (violation of contract terms, interruptions in transport, etc.).
Calculation of revenue using the formula
Let's look at how to find revenue from sales of products using the formula. When making calculations, it is necessary to take into account the current sales volume and prices. The general formula for revenue from product sales looks like this:
B = Q × P
Here:
Q – number of goods sold;
P – selling price.
The formula can be used to evaluate an organization's performance and build long-term plans.
In practice, accounting for revenue from the sale of products, works and services is carried out using two methods:
- cash method (if the moment of sale is recognized as the fact of receipt of money to the seller’s bank account);
- accrual method (if the moment of recognition of income is the fact of shipment of goods).
Methods for receiving proceeds to a current account
In accounting, revenue is income received from ordinary activities - from the sale of products and goods, performance of work, provision of services (clause 2, 5 of PBU 9/99).
Revenue recognition is always reflected by an entry in the credit of account 90 “Sales”, subaccount “Revenue”. Debit shows the amount owed by the buyer. That is, the wiring is like this:
- Debit 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” Credit 90, subaccount “Revenue”
.
But the proceeds can be transferred to the current account in different ways.
Methods for receipt of proceeds to the current account may be as follows:
- transfer from the counterparty's current account;
- cash from the cash register;
- via terminal;
- through collection.
That's why the wiring will be different.
Examples of revenue calculation
Examples of calculating revenue from product sales in different ways are given below.
Example 1
LLC "Electrod" is engaged in the production of lamps. During the reporting year the following products were sold:
- lamp “Ella” – 700 pieces at a price of 250 rubles;
- lamp “Teresa” – 600 pieces at a price of 340 rubles;
- lamp “Miranda” – 400 pieces at a price of 600 rubles.
The annual revenue will be calculated as follows:
B = (700 × 250) + (600 × 340) + (400 × 600) = 619 thousand rubles.
Example 2
IP Petrov A.A. applies the cash method of accounting for income and expenses. On January 25, 2022, the entrepreneur delivered goods to the buyer for a total amount of 180 thousand rubles. On March 5, 2022, the individual entrepreneur agreed with the buyer on a mutual settlement in the amount of 106.2 thousand rubles. (including VAT - 16.2 thousand rubles). What revenue should an entrepreneur report?
As of the date of the offset agreement with the buyer (March 5, 2022), the individual entrepreneur is obliged to take into account income in the amount of the repaid debt (excluding VAT): 106,200 – 16,200 = 90,000 rubles.
Example 3
On February 12, 2022, Teplomash LLC shipped goods to Ryabina LLC in the amount of 600 thousand rubles. Ryabina LLC paid off with Teplomash LLC on April 3, 2022, transferring money to its bank account. Teplomash LLC uses the accrual method when accounting for income, so all revenue will be displayed in accounting and tax accounting in February.
Sales of finished products produced during the month of production
Regulatory regulation
Sales are recognized as the transfer of ownership of goods on a reimbursable basis (Article 39 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Finished products are part of the organization’s inventories, which are the end result of the production cycle and have quality characteristics that comply with the terms of the contract (clause 199 of the Methodological Guidelines for the Accounting of Inventory Production, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 28, 2001 N 119n). Sales of finished products are reflected in the same way as sales of goods.
Organizations engaged in production activities, for the purpose of calculating income tax, take into account income and expenses associated with the production and sale of finished products.
Income:
- In the accounting system, revenue from the sale of finished products is classified as income from ordinary activities (clause 5 of PBU 9/99) and is recognized at the moment of transfer of ownership of the product (clause 12 of PBU 9/99).
- In NU, income is revenue from sales excluding VAT (Clause 1, Article 248 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Article 249 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The date of receipt of income using the accrual method is the date of sale of products (Article 271 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Expenses:
- In accounting, this is the actual cost of finished products (clause 5, clause 9 of PBU 10/99). The method for assessing finished products in the warehouse (clauses 203, 204 of the Methodological Guidelines for the Accounting of Inventory Plants, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 28, 2001 N 119n) is established in the accounting policy.
- In NU, expenses that reduce sales revenue include the amounts of expenses associated with the production and sale of products (Article 318 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation): direct and indirect. Direct costs included in the cost of finished products are written off as they are sold.
Accounting in 1C
Sales of finished products are documented in the document Sales (act, invoice) transaction type Goods (invoice) in the section Sales – Sales – Sales (acts, invoices).
The header of the document states:
- Agreement - a document according to which settlements are made with the buyer, Type of agreement - With the buyer .
In our example, calculations are carried out in rubles, which is noted in 1C in the PDF delivery agreement. Therefore, in the Sales document (act, invoice) the following sub-accounts are automatically established for settlements with the buyer:
- Settlement account - 62.01 “Settlements with buyers and customers.”
- Advances account - 62.02 “Calculations for advances received.”
If necessary, accounts for settlements with the buyer can be corrected in the document manually or configured for the automatic insertion of other accounts for settlements with the counterparty.
The tabular part indicates the products sold from the Nomenclature directory.
- Accounts are filled in the document automatically, depending on the settings in the Item Accounts .
For the item type Products PDF, the default Accounting Account “Finished Products”, but it can be changed manually in the document.
Find out more about setting up item accounting accounts
- Income account - 90.01.1 “Revenue from activities with the main tax system.”
- Expense account - 90.02.1 “Cost of sales for activities with the main tax system.”
- VAT account - 90.03 “Value added tax”.
- Nomenclature groups - a nomenclature group related to the sale of products produced in-house, selected from the Nomenclature Groups directory. The item group is automatically filled in . PDF
The nomenclature group related to the sale of products of own production must be indicated in the Nomenclature groups for the sale of products and services PDF in the Main section - Settings - Taxes and reports - Income Tax tab - link Nomenclature groups for the sale of products and services. The correct completion of the income tax return depends on this setting.
Read more Setting up accounting policies
Postings according to the document
If the sale of products is carried out in the month of its production, i.e. before the formation of the actual cost, then the amount for posting Dt 90.02.1 Kt will be equal to:
- The planned cost of finished products, if the planned cost of production is used when calculating output.
- Zero if the planned cost of production is not used when calculating output. PDF
The document generates transactions:
- Dt 90.02.1 Kt - write-off of the cost of finished products, without amount: production was carried out without using planned prices. PDF
- Dt 62.01 Kt 90.01.1 - revenue from the sale of finished products: in accounting accounting, including VAT;
- in NU excluding VAT;
If there is a balance of finished products in accounting at the beginning of the month, then in the Sales document (act, invoice) the cost of goods sold will be formed taking into account this balance and Inventory Valuation Method established in the Accounting Policy. But the final cost will be formed after completing the Month Closing procedure.
Documenting
The organization must approve the forms of primary documents, including the product sales document. The following basic forms are used in 1C:
- Consignment note in the form TORG-12. PDF
- Universal transfer document. PDF
Forms can be printed by clicking the Print button – Consignment note (TORG-12) and Print – Universal transfer document (UDD).
Income tax return
In the income tax return, the amount of proceeds from the sale of goods is reflected as income from sales:
Sheet 02 Appendix No. 1:
- page 010 “Proceeds from sales - total”, including: page 011 “... revenue from the sale of goods (works, services) of own production.” PDF
Reflection in accounting
Account 90 “Sales” is used to record revenue from sales of products. The account consists of several sub-accounts. Postings for revenue from sales of products are compiled in order to determine the financial result from sales. The mandatory conditions under which revenue is recognized in accounting are given in PBU 9/99.
Example 1
Rubezh LLC sold spare parts for the amount of 354 thousand rubles. (including VAT – 54 thousand rubles). Revenue is recorded at the time of shipment. The cost of goods is 210 thousand rubles, sales costs are 35 thousand rubles. The buyer transferred the money to the seller.
The entries for revenue from the sale of finished products will be as follows:
- Dt 62 Kt 90 – revenue from the sale of finished products is reflected on the day of shipment - 354 thousand rubles.
- Dt 90 Kt 68 - the amount of VAT is reflected - 54 thousand rubles.
- Dt 90 Kt 43 - the actual cost of spare parts is displayed - 210 thousand rubles.
- Dt 90 Kt 44 - sales expenses written off - 35 thousand rubles.
- Dt 51 Kt 62 – funds received from buyers for the products received amounted to 354 thousand rubles.
Calculation of financial results: 354,000 – 54,000 – 210,000 – 35,000 = 55,000 (rub.).
After the postings reflect the revenue from the sale of finished products, we take into account the financial result:
- Dt 90 Kt 99 - a profit of 55 thousand rubles was received.
Example 2
The organization sold spare parts in the amount of 354 thousand rubles. (including VAT – 54 thousand rubles). Revenue is recognized at the time of payment, and selling expenses are written off entirely to cost of goods sold. The cost of spare parts is 210 thousand rubles, sales costs are 35 thousand rubles. The buyer transferred 300 thousand rubles.
The postings will be like this:
- Dt 45 Kt 43 - the amount of the actual cost of goods shipped is written off - 210 thousand rubles.
- Dt 51 Kt 62 - buyers transferred money to pay for goods - 300 thousand rubles.
- Dt 62 Kt 90 - accounting records reflect the proceeds from the sale of finished products by posting - 300 thousand rubles.
- Dt 90 Kt 68 – the amount of VAT is reflected. The calculation is as follows: (300,000: 118 × 18) = 45,762 rubles.
- Dt 90 Kt 45 - reflects the amount of the actual cost of products, the proceeds from the sale of which are recognized in accounting. The calculation is as follows: (210,000 × 300,000: 354,000) = 177,966 rubles.
- Dt 90 Kt 44 – the amount of sales expenses of 35 thousand rubles was written off.
Let's calculate the financial result: 300,000 – 45,762 – 177,966 – 35,000 = 41,272 rubles.
- Dt 90 Kt 99 – profit from sales of 41,272 rubles is reflected.
Finished product accounting
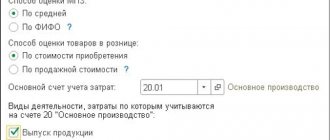
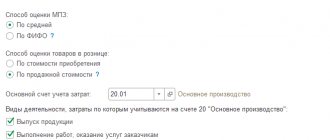
From the point of view of PBU 5/01 “Accounting for inventories,” finished products are considered to be the organization’s inventories, the purpose of which is to be sold to make a profit. In the balance sheet, actual or planned cost is used to account for SOEs. The chosen method determines the further reflection of the goods on balance sheet accounts. WTP can be assessed using any of the following methods:
Actual cost
- Actual production cost. This is the totality of all expenses (including general expenses) for the production of a product. They are posted to account 20 “Main production”, which contains information about all production costs. Used for small production volumes.
- Incomplete production cost. This is a complex of all production expenses with the exception of general business expenses: salaries of management personnel, vacation and travel allowances, depreciation, etc. Thanks to such an assessment, “net” production costs are determined, which allows for effective planning of activities with the limited resources available.
What costs form the total cost of finished products ?
At discounted prices
- Planned production cost. The method is applicable for large production volumes. The essence of the method is to determine the difference between actual and accounting costs, which then must be written off. Postings are made to account 40 “Release of products (works, services)” or to account 43 “Finished products”.
- Valuation at wholesale, negotiated prices. Applicable when selling prices are stable. But at the same time, it does not characterize the cost of GP. The method is based on the difference in types of costs, which are most often negative.
- Estimated at retail prices. The principle of operation of the method is similar to those described above in this category. Actively used today.
IMPORTANT! When determining the accounting prices of an item, it is important to adhere to a certain ratio of actual and accounting costs. In other words, products that have the same actual cost must have the same book price.
Revenue planning
The head of the organization or special services can plan revenue from the sale of products, works, and services. In an unstable economic situation, quarterly planning will be more effective than annual planning.
To plan revenue from product sales, the following methods are used:
- Direct counting method. Applicable in case of guaranteed demand. Products are produced in the quantities specified in pre-orders. Revenue is calculated by multiplying the volume of products sold by its price.
- Calculation method. It is used in conditions of uncertainty of demand for manufactured goods. The prospects for their implementation are taken into account.
Revenue analysis
Analysis of revenue from product sales allows you to solve the following problems:
- determine the validity of the business plan indicator for the sale of goods;
- determine the degree of plan fulfillment in terms of the volume and range of products sold;
- establish the influence of individual factors on the deviation of actual sales volume from the planned one;
- identify reserves for further increase in sales.
One of the effective methods of economic analysis is factor analysis of revenue from product sales.
It helps to determine the influence of specific factors on changes in revenue. In the process of analysis, much attention is paid to the following factors: volume of sales of goods, selling prices, cost, structure of products sold. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.