For employees, a corporate party is a holiday. And the accountant’s concern is what about VAT, income tax, personal income tax, and insurance premiums.
If for most employees a corporate event is just relaxation and fun, then for the accounting department it also means renting premises, its decoration and expenses for servicing employees during the event.
The justification for the upcoming expenses for a corporate event is an order to hold the event, signed by the company’s management or an authorized person. The form for drawing up this order is not legally approved, so the document can be drawn up in free form in accordance with the internal requirements of the company’s document flow and if the required details are available (document number and date of preparation). Accounting for expenses for corporate events is carried out in the general manner - on the basis of primary documents confirming these expenses. In addition to the order and supporting documents, the kit can be supplemented with a cost estimate, however, this document is not mandatory from the point of view of legal requirements and can be drawn up in accordance with the company’s internal document flow regulations.
The concept of “corporate party” is used to refer to entertainment events organized by the company’s management for employees in order to motivate them. As a rule, corporate events take place in the form of parties in a cafe or restaurant and may include the following expenses:
- rental of premises for an event;
- expenses for organization and service (celebrity host, musicians, waiters, catering);
- payment for the banquet;
- expenses associated with decorating the premises for the holiday (decorating the hall in a corporate style, etc.);
A corporate event may include other expenses that, in the opinion of company management, are necessary for the event.
Holiday for the tax office
Tax legislation expenses of an organization that are of a social nature and made for the benefit of an employee or other persons (including payment for travel packages, membership in a fitness club, purchase of gift certificates for vacations and visits to beauty salons, compensation for the use of a personal car, payment for children’s education in preschool institutions and schools), does not take into account profits for tax purposes, regardless of whether they are provided for in employment contracts or not.
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation (Article 264) establishes a list of expenses, the reflection of which is permissible in tax accounting if the necessary supporting documents are available. Expenses for a corporate event are not included in this list; therefore, in general, a company that has incurred expenses for holding a corporate event for employees cannot take these expenses into account in terms of reducing the tax base. This position is widely confirmed by judicial practice (in particular, the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the West Siberian District dated November 19, 2013 No. A67-7663/2012).
At the same time, the opportunity to reduce income tax by taking into account expenses for a corporate event still exists, provided that the event is framed as a business meeting with partners or organized with the aim of attracting new clients. In this case, the following documents are required:
- an order to hold a representative event for existing partners and attract new clients;
- estimate for entertainment expenses;
- contracts, certificates of completion of work, which indicate that expenses were incurred in connection with an official (not entertainment) event.
Tax accounting for corporate expenses is possible provided that the amount of these expenses does not exceed 4% of the payroll amount.
Tax accounting
We apply PBU 18/02, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 19, 2002 No. 114n, in order to correctly reflect the costs of corporate events in the tax accounting of the organization. The actual cost of goods and VAT accrued upon their transfer for own needs are recognized in accounting and are not taken into account for profit tax purposes. In accounting, a constant difference and a corresponding constant tax expense (FRT) arise. The main transactions, how to register in a tax banquet hall, for income tax and VAT look like this:
Let's consider tax accounting for holiday expenses when applying a simplified taxation system. This is relevant for organizations that are required to keep records of costs and taxes. The answer to the question of how to reflect payment for a New Year's corporate party under the simplified tax system can be found in PBU 10/99: the costs of holding festive events are recognized as other expenses. Organizations using the simplified tax system reduce the income received by the expenses listed in paragraph 1 of Art. 346.16 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. But corporate expenses are not mentioned in this article, therefore the tax cannot be reduced on them, and postings for holding a banquet under the simplified tax system “expenses” have nothing to do with taxation. An accountant performs only accounting transactions.
Taxation options for a corporate holiday
| Who will come to the corporate party | How to account for expenses and what taxes to pay | ||||
| Income tax | VAT | Personal income tax | Insurance premiums | ||
| The event is intended for a specific circle: only employees or only management | Expenses cannot be taken into account when determining the taxable base for profit, and VAT is not accepted for deduction (clause 29 of article 270, clause 2 of article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 02/08/2016 No. 03-03-06/1/6140 , dated December 13, 2012 No. 03-07-07/133) | Taxed as income in kind (Letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 14, 2013 No. 03-04-06/33039, dated April 3, 2013 No. 03-04-05/6-333, Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated July 27, 2007 No. 28-11/071808) | If the company's expenses for a corporate party on the occasion of a holiday are not targeted payments in favor of specific employees, there are no contributions. If they are - from the amount of expenses for each employee you need to pay insurance premiums (Letter of the Ministry of Labor dated May 24, 2013 No. 14-1-1061) | ||
| The event is intended for an indefinite number of people | Expenses cannot be taken into account when determining the taxable base for profit; VAT is not deductible (clause 29 of article 270, clause 2 of article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 02/08/2016 No. 03-03-06/1/6140, dated December 13, 2012 No. 03-07-07/133) | The participants of the corporate party did not receive any income, it is impossible to determine to which circle of people the service is directed, there is nothing to tax with personal income tax (Letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 08/14/2013 No. 03-04-06/33039, dated 04/03/20313 No. 03-04-05/6- 333) | The participants of the corporate party have no income, it is impossible to determine to which circle of people the service is directed, and in any case this is not related to the employees performing their labor functions (Letter of the Ministry of Labor dated May 24, 2013 No. 14-1-1061, Determination of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated November 26, 2012 No. VAS-16165/12 in case No. A14-13077/2011) | ||
| The event is official in nature with the invitation of business partners | Expenses as entertainment expenses are taken into account within 4% of labor costs (subclause 22, clause 1, article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation in the presence of supporting documents (Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) | If expenses are representative, VAT is deductible in full (Clause 7, Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). But remember, entertainment expenses must be documented (Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) | There is no income or personal income tax because: employees act in the interests of the organization; employees are required to take part in events, but only if they have documents confirming expenses (Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 08/07/2012 No. 03-04-06/6-221, dated 12/11/2012 No. 03-04-06/4-348) | There is no obligation to pay insurance premiums (Letters of the Federal Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation dated November 17, 2011 No. 14-03-11/08-13985, Ministry of Health and Social Development dated 06.08.2010 No. 2538-19) | |
Personal income tax and insurance premiums
Let’s figure out whether corporate event expenses are subject to insurance premiums. For that part of the holiday that the employer was unable to hold as an entertainment event, the employees will have to pay tax. When an employer pays for the rent of a hall, banquet services and menus, Santa Claus, fireworks and a champagne fountain, he does it as if for his employees. This means that they receive benefits equal to the cost of all this per person. Since there is a benefit, then, by virtue of Article 210 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, tax must be paid on it, since the object of personal income tax and insurance contributions is the taxpayer’s income received by him both in cash and in kind. And Article 211 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation directly states that income in kind includes payment by the employer for rest, travel compensation and other material benefits to employees that are not directly related to the performance of their official duties, including corporate events.
Therefore, the employer is obliged to divide the entire amount of costs by the number of participants in the celebration and find out what benefit each of them received. Further, as a tax agent, he is obliged to calculate and withhold personal income tax from employees and transfer it to the budget. Experts from the Ministry of Finance write about this (letters from the Ministry of Finance dated 04/03/2013 No. 03-04-05/6-333, dated 03/06/2013 No. 03-04-06/6715).
But personal income tax has the right to collect only if there is a list of guests of the corporate party: in this case, the taxation of the event will partly fall on their shoulders. If the banquet is open to everyone, there is no opportunity to calculate the benefit received by each of the participants, which means they do not have the obligation to pay personal income tax and insurance premiums. Therefore, it is advisable to avoid detailed lists of employees and indications in documents of the exact number of people. This position is confirmed by letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-04-06/33039 dated 08/14/2013. It is also not possible to calculate insurance premiums, which is confirmed by court decisions: Resolution of the AS UO No. F09-1827/15 dated 04/21/2015.
What taxes arise
As a general rule, VAT follows income tax. This means that if a company does not take into account the costs of a corporate event for profit tax purposes, then VAT cannot be deducted. The reason is as follows: in this case, the conditions established in paragraph 2 of Art. 171 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
If the company takes into account entertainment expenses, then value added tax is deducted within the established limit. The courts believe that the right to deduct VAT does not depend on the economic justification of expenses, but only on whether the taxpayer complied with the provisions of Art. 171 and 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation on tax deductions, whether VAT was transferred to the budget.
In practice, it is difficult to prove the connection of economically unjustified expenses with the production activities of a company subject to VAT. Tax authorities may make claims. Therefore, the choice is up to the company - either act conservatively (not deduct VAT) or go to court.
When a company buys goods and transfers them to the event organizer (for example, food to a restaurant for preparing dinner), there is no VAT subject to taxation. There is no fact of sale of products within the meaning of Art. 39 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation: the company does not transfer ownership of goods on a reimbursable basis. Therefore, there is no need to charge VAT on such an operation. The courts agree with the conclusion.
The courts have also repeatedly emphasized that there is no need to calculate VAT on the cost of a festive dinner organized for employees of an enterprise, since these transactions do not constitute sales.
The object of VAT taxation does not arise (Resolutions of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the West Siberian District dated 04.03.2009 No. F04-1315/2009, FAS Northwestern District dated 11.12.2008 No. A56-19219/2008, FAS Ural District dated 05.09.2007 No. F09-7170 /07-С2).
At the same time, non-assessment of VAT deprives an organization of the right to deduct tax on goods, works, and services purchased for a corporate event (subclause 1, clause 2, article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). It is also impossible to take into account “input” VAT for profit tax (clauses 1, 2 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
A corporate holiday is not a production-oriented event, therefore it is impossible to take into account the expenses associated with it for taxation:
- they do not meet the requirements of paragraph 1 of Art. 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation on the economic justification of costs (Letters of the Ministry of Finance dated September 11, 2006 No. 03-03-04/2/206, dated December 20, 2005 No. 03-03-04/1/430);
- these expenses can be qualified as made for the benefit of employees. And they are directly prohibited from being taken into account by clause 29 of Art. 270 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
There will be no obligation to withhold personal income tax from employees on gifts received at a corporate party, since in order to calculate the tax, it is necessary to determine the amount of income of each of them. And the Ministry of Finance advises taking all possible measures for this (for example, in Letters dated 04/03/2013 No. 03-04-05/6-333, dated 03/06/2013 No. 03-04-06/6715). However, in the case of a corporate event, there is no opportunity to personalize the economic benefit, so the calculation is very difficult. Officials agree with this (Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated August 3, 2018 No. 03-04-06/55047).
It is necessary to withhold personal income tax if the event is an off-site event: payment for workers’ travel to the location of the corporate event, as well as accommodation there, are the workers’ income in kind (Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated 04/21/2017 No. 03-04-06/24140).
If a company excludes income from the tax base, the tax office may charge additional personal income tax. To prevent this from happening, measures must be taken to prevent claims from arising. In particular, the documents should not indicate the lists of those present at the corporate event, as well as the number of participants.
Children's activities
One of the pleasant New Year's bonuses for employees with children is the company's provision of tickets to various New Year's events (Christmas trees). How are these transactions accounted for and reflected? To simplify accounting and minimize risks, employees, and not their children, must be indicated as recipients of holiday tickets for the Christmas tree in various organizational, legal and local documents of the company. If the cost of tickets for the Christmas tree exceeds 3,000 rubles, the parties must conclude a gift agreement between themselves in writing, because failure to comply with the written form leads to the nullity of the agreement (Article 574 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). The cost of tickets for the New Year tree is repaid from the net profit of the enterprise, because their issuance is in no way related to activities that can increase the organization’s income, and they are transferred free of charge (clause 16 of article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). VAT must be calculated from the cost of the tickets transferred (subclause 1, clause 1, article 146). If the price of a New Year's ticket exceeds 4,000 rubles, personal income tax must be withheld from the excess amount (clause 28 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Insurance premiums are not charged on the cost of Christmas trees (letter of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated July 8, 2015 No. 17-3/B-335), since in this case the connection of the gift with the employee’s work activity will not be traced.
note
To simplify accounting and minimize risks, employees, and not their children, must be indicated as recipients of holiday tickets for the Christmas tree in various organizational, legal and local documents of the company.
Annual Employee Conference
At the annual corporate party, the results of the year are summed up, employees are introduced to the company's plans, or those who have particularly distinguished themselves are awarded.
The event strengthens employee loyalty to the company, which means it has production goals. But the tax authorities do not believe that corporate expenses are economically justified and will lead to income in the future. And they do not recognize the corresponding costs for income tax purposes. The courts support the fiscals. For example, the inspectorate challenged the company’s expenses for holding a corporate event. The taxpayer indicated that the event increased employee engagement and motivation. The court found the arguments unfounded and noted that the festive events are not related to the production process, which means that the costs for them do not meet the criteria of Art. 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Judicial practice allows only the official part of the costs of a corporate event to be taken into account in expenses for income tax purposes. For example, if an employer presents a new strategy or conducts training, then such expenses will include the cost of renting a hall and speaking by business trainers.
Collect documents that will help protect the deduction of expenses for the official part of events from claims from fiscal officials. For example:
- order for the event;
- detailed event plan;
- an estimate with a detailed breakdown of the cost of each part of the holiday;
- A report containing training questions or presentations that employees have reviewed.
Photographs that demonstrate the training process and summing up production results can also prove the validity of costs.
At the same time, the “entertainment” part, for example, a banquet, guest stars, expenses for a DJ, games and competitions, memorable gifts for all employees, is not included in the costs. The reason is that expenses for organizing entertainment and recreation cannot be taken into account as expenses. The courts agree with the tax authorities. Therefore, it is important to divide the costs: in order to “save” at least some part, you need to carefully prepare documents.
Special documents
As follows from the table, the taxation system for corporate holidays and related payments is not simple. In terms of accounting for personal income tax and insurance premiums, it directly depends on the type and type of event. As for income tax, expenses can only be taken into account if they are classified as representative expenses, which will be very difficult to do. For these purposes, at a minimum, special documents should be drawn up. One of them is an order to hold a representative event, containing the specific goals and objectives of its holding, the date and place of the holiday. In addition, you need to prepare a cost estimate, which should include all the costs planned for implementation. It is imperative to create a list of participants for the event, but it should be taken into account that if the participants are only company employees, then there will be no opportunity to take into account expenses as entertainment expenses.
Immediately after the event, you should take care of documents confirming the very fact of holding a corporate event. Such papers may be a report on a representative event, drawn up in any form, but containing all the details provided for by the Federal Law “On Accounting”, which describes in as much detail as possible the events that occurred and the results achieved / not achieved.
Another option would be a financial report on all expenses incurred at events, to which contracts with contractors, cash receipts, and payment documents are attached. Photos from the past event will also be a fact of the event.
Marketing events for partners or clients of the company
The purpose of these events is to advertise your own activities. This could be a gala evening, a banquet or a gala dinner. The taxpayer has the right to recognize the expenses incurred as representative expenses. However, the amount of such expenses cannot exceed 4% of labor costs for the reporting period.
If the event is attended not only by partners, but also by company employees who communicate with clients, the taxpayer can also receive a deduction. It can be argued that employees develop the organization's business contacts and improve its business results. In this case, employee expenses can be deducted from the income tax base. The courts confirm that the costs of the event are justified.
Prepare the documents so that they satisfy the goals and format of the event: make a list of invited and arriving guests, guest reviews of the celebration, event plan, photo report.
Salary taxes
The letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-04-06/33039 dated August 14, 2013 determines whether corporate event expenses are subject to personal income tax - no, the costs of organizing a corporate event cannot be personalized. In this regard, there is no need to calculate personal income tax.
If the company compensates for any expenses of a specific employee (for the purchase of a personalized ticket for travel to the event venue, payment and write-off of accommodation at a corporate event), then such payments are recognized as the employee’s income. In this case, personal income tax on transfers and excursions to corporate events and on the cost of accommodation is calculated in the usual manner.
There is no need to charge insurance premiums to pay for a corporate event, since they are not only difficult to personalize, but are also not related to the performance of job duties. Even in the case of claims from inspection bodies, the courts side with the company in this matter (resolution of the AS UO No. F09-1827/15 of 04/21/2015 in case No. A71-7725/2014). Thus, you do not have to pay either insurance premiums or personal income tax for a corporate party in a restaurant with employees.
Gifts for children
A gift is income in kind, which is taken into account when determining the tax base for personal income tax (Clause 1, Article 210 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, paragraph 28 of Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation exempts from taxation gifts received by individuals from organizations whose value does not exceed 4,000 rubles per year. It is unlikely that a children's New Year's gift will cost more. This means that the employee most likely will not be required to withhold personal income tax. In this case, the organization is required to keep personalized records of these incomes (for example, Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated January 20, 2017 No. 03-04-06/2650).
If the gift costs more than 4,000 rubles. (in this case, a written gift agreement is required - clause 2 of Article 574 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation) or the organization gives gifts to the children of employees not only for the New Year, but also other holidays and the total cost of gifts for the year exceeded the tax-exempt amount, the organization becomes a tax agent ( Clause 1 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). But only in relation to the excess amount, from which the tax must be calculated.
If a child receives only a gift, the organization does not make any monetary payments to him. Consequently, she has no opportunity to withhold personal income tax (clause 4 of article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). But there is an obligation to inform the taxpayer and the tax authority about this (clause 5 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
After this, the child’s legal representatives will have to pay the tax: parents, adoptive parents, guardians, trustees (Articles 27, 29, subparagraph 4, paragraph 1, Article 228 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Federal Tax Service dated April 23, 2009 No. 3-5-04/ [ email protected] ).
There is no need to pay insurance premiums for holiday expenses for the same reason. During the period of validity of Law No. 212-FZ, this was confirmed by the Ministry of Labor (clause 4 of Letter No. 14-1-1061 dated May 24, 2013). These conclusions are still valid today.
There is no need to calculate insurance premiums, including for injuries, from the cost of children's gifts. If only because there is no labor relationship between the children of employees and the organization, therefore, there is no object for taxation of contributions (clause 1 of Article 420 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 1 of Article 20.1 of the Federal Law of July 24, 1998 No. 125-FZ, Letter of the Ministry of Health and Social Development RF dated May 19, 2010 No. 1239-19).
In addition, paragraph 4 of Art. 420 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation directly provides that payments under civil contracts, within the framework of which the transfer of ownership of property occurs, do not relate to the object of contributions. And a gift agreement is just such an agreement.
Based on the chart of accounts and instructions for its use (approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n), the purchase and issuance of children's gifts can be reflected in accounting as follows:
Debit 41 Credit 60 - children's New Year's gifts were capitalized
Debit 19 Credit 60 - reflected VAT presented by the supplier
Debit 68, subaccount “Calculations for VAT”, Credit 19 - “input” VAT is accepted for deduction
Debit 73 Credit 41 - reflects the transfer of gifts to employees
Debit 91 Credit 73 - the cost of gifts is included in other expenses
Debit 91 Credit 68, subaccount “Calculations for VAT” - VAT is charged on the cost of gifts
Due to the fact that these expenses do not reduce taxable profit, organizations applying PBU 18/02 (approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 19, 2002 No. 114n) will have a permanent tax difference and a corresponding permanent tax liability (PNO):
Debit 99, subaccount “Permanent tax liability” Credit 68, subaccount “Calculations for income tax” - for the amount of PTI.
If the gift is a voucher , then if certain conditions are simultaneously met, it is not subject to personal income tax for both the employee and his family members. Namely (clause 9 of article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- The voucher must be paid for at the expense of the organization if the costs of payment in accordance with Ch. 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are not taken into account when calculating income tax; funds from activities under special tax regimes; budget funds, including at the expense of the Federal Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation; funds of religious and other non-profit organizations specified in paragraph 9 of Art. 217 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- Voucher services are provided by a sanatorium-resort or health-improving organization located on the territory of the Russian Federation. Documents that confirm the sanatorium-resort or health status of an organization may be a license of the organization, constituent documents containing an indication of the type of activity carried out by the organization (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 11, 2014 No. PA-4-11 / [email protected] ).
- The tour is not a tourist one.
- Payment for the trip is confirmed, for example, by an agreement with a sanatorium (health) organization, payment documents (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 19, 2014 No. 03-04-06/46990).
It is important to note that payment to an employee of the cost of sanatorium-resort vouchers is subject to insurance contributions for compulsory pension, medical insurance and VNIM, as well as for accident insurance (hereinafter referred to as insurance premiums), since:
- carried out within the framework of labor relations, which means it is subject to insurance premiums (subclause 1, clause 1, article 420 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 1, article 20.1 of law No. 125-FZ);
- is not included in the number of payments that are not subject to insurance premiums (Article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and Article 20.2 of Law No. 125-FZ.)
Note that the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation, analyzing similar provisions of Law No. 212-FZ, which became invalid on January 1, 2022, came to the conclusion that social payments based on a collective agreement, which are not incentives, and which do not depend on the qualifications of workers, are not remuneration of employees (remuneration for labor) and are not subject to contributions for compulsory pension, health insurance and VNIM (Resolution No. 17744/12 of May 14, 2013).
From 2022, in accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 1, art. 2 of Federal Law No. 113-FZ of April 23, 2018, income tax expenses take into account the cost of tourist and health resort vouchers in Russia purchased for employees and members of their families, but not more than 50 thousand rubles per person per year. The entire amount of such expenses, together with expenses under contracts for the provision of medical services for a period of at least a year and expenses for voluntary personal insurance for medical expenses, should not exceed 6% of labor costs.
According to the law, the cost of a gift to business partners should not exceed 3,000 rubles, since donations of a larger amount in relations between commercial organizations are prohibited (subclause 4, clause 1, article 575 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
There are no penalties for violating this requirement. Moreover, according to the norms of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a gift in circumvention of this prohibition may lead to the invalidity of the transaction (Article 168 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). As for the taxation procedure, the cost of the gift does not affect it - an expensive gift is taxed on a general basis.
How to reflect corporate event expenses in accounting
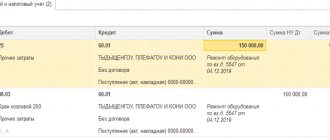
Expenses associated with corporate events are reflected in the debit of account 91/2 “Other expenses” and the credit of account 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” or 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”.
Due to the fact that expenses for corporate parties (entertainment events) are not taken into account when reducing the tax base, but are reflected in accounting in full, the customer company has a permanent tax liability in the amount of 20% of the amount of expenses reflected in accounting.
One of the popular questions among accountants is whether a company that holds a corporate party for employees has the right to a VAT tax deduction on the amount of expenses incurred. The response of legislators and the position of the fiscal service and the Ministry of Finance on this issue is clear - the amount of VAT on expenses for entertainment events (including corporate events) cannot be deducted (letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-07-07/133 dated December 13, 2012).
Let's look at a few examples.
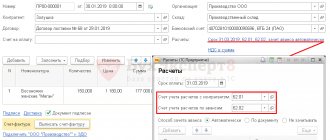
Example No. 1. Reflection of expenses for toastmaster-IP services on the simplified tax system
held a New Year's corporate party for employees, in connection with which the company paid for the services of the toastmaster (IP Sidorchuk on the simplified tax system) in the amount of 12,305 rubles.
| No. | Dt | CT | Sum | Description |
| 1 | 91.2 | 60 | RUB 12,305 | Based on the contract and the certificate of completion of work, the expenses for the corporate event (toastmaster services) are reflected in the Karat accounting system. |
| 2 | 60 | 51 | RUB 12,305 | transferred payment for holding a corporate event to the account of IP Sidorchuk |
| 3 | 99 | 68 | RUB 2,431 | Reflected PNO - permanent tax liability (RUB 12,305 * 20%) |
Example No. 2. Reflection of expenses for field service (performer – legal entity on OSNO)
To organize the anniversary celebration, he hires Buket LLC to organize on-site catering for a corporate event. Cost – 24,808 rubles, incl. VAT 3.785 rub.
| No. | Dt | CT | Sum | Description |
| 1 | 91.2 | 60 | RUR 21,023 | Based on the contract and the certificate of completion of work, the “Stimulus” accounting reflects the expenses for the corporate event (field service services without VAT) |
| 2 | 19 | 60 | RUR 3,785 | The amount of VAT presented by the organizer of the service (LLC “Buket”) is taken into account |
| 3 | 91.2 | 19 | RUR 3,785 | The amount of “input” VAT is written off as other expenses |
| 4 | 60 | 51 | RUR 24,808 | transferred payment for organizing on-site catering for a corporate event to the account of Buket LLC |
| 5 | 99 | 68 | RUB 4,962 | Reflected PNO - permanent tax liability (RUB 24,808 * 20%) |
What's a corporate party without a banquet?
Costs for corporate events can vary greatly. Only imagination and a wallet can stop it. A small company will have a modest evening at the office, a larger company will order dinner at a restaurant, the very rich will take their employees to a boarding house or even a hotel abroad.
But the more spent on a corporate event, the more carefully the regulatory authorities will check these expenses.
You can find out how to arrange a corporate event in our publication “Order for a corporate event.”
List of entertainment expenses
First of all, you need to remember that there is a clearly defined list of expenses that can be classified as entertainment expenses for income tax purposes. It is contained in paragraph 2 of Art. 264 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In general, these are expenses “for the official reception and (or) service of representatives of other organizations participating in negotiations in order to establish and (or) maintain mutual cooperation, as well as participants who arrived at meetings of the board of directors (board) or other governing body taxpayer, regardless of the location of these events.”
To be more specific, expenses for an official reception mean expenses directly for its holding, that is, for holding a breakfast, lunch or other similar event. It turns out that a business event can take place in a cafe or restaurant. The main thing is to confirm that the dinner at the restaurant was business-oriented. Moreover, with proper registration, a representative event can be a dinner in a restaurant, including the consumption of alcoholic beverages (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 1, 2010 No. 03-03-06/1/675). Officials also allow the cost of alcohol to be classified as entertainment expenses (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated January 22, 2019 No. 03-03-06/1/3120).
As for the expenses for servicing invited persons, which also relate to entertainment expenses, they do not mean absolutely all expenses, but only:
- for transport support for the delivery of persons to the venue of the entertainment event and back;
- buffet service during negotiations;
- payment for the services of translators who are not on the taxpayer’s staff.
At the same time, in paragraph 2 of Art. 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation directly states that expenses for organizing entertainment, recreation, prevention or treatment of diseases cannot be considered entertainment expenses.
Next, we present the necessary package of documents that will help companies avoid questions from inspectors, and also consider the most common violations.
We invest in banquet services
Well, the festive mood has been created - it’s time for the corporate event itself.
Let's digress a little and remember that the Tax Code includes labor costs as the cost of food and products provided free of charge in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, as well as other expenses stipulated by the labor and (or) collective agreement (clauses 4 and 25 of Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation ). We remembered this in order to estimate: maybe we could include the “holiday table” in labor costs? But, you must admit, in reality, the employment of accounting and personnel services does not allow each holiday to be stipulated in the employment contract as a form of remuneration in kind, and at the same time managing to receive corresponding statements from employees. Therefore, we will assume that the costs of the festive table are not provided for in employment contracts, therefore, it will not be possible to attribute the banquet to wages.
At the moment, the position of the majority of tax inspectors is that the organization should act as a tax agent and withhold money from employees for free meals provided, since from the point of view of the tax authorities, a corporate party is income in kind, and not a means of strengthening the team, as they think many.
And everything would be fine, but how to calculate who got and how much food? What if someone didn't come? Get it off him, and then figure out where he was and why he didn’t eat or drink. This is not a corporate event, but sheer hard labor with the accompanying creation of stressful situations for the following days.
If you ask the Federal Tax Service, you will most likely receive the answer that you do not need to monitor every employee - you just need to divide the amount of the banquet by the number of participants, which must be determined in advance. In this case, tax officials rely on subparagraph 1 of paragraph 2 of Article 211 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. But don't rush to agree with the inspectors. Since the determination of the tax base for personal income tax by calculation is not provided, we will not withhold and transfer personal income tax to the budget from such income. In practice, confirmation of this position can be found in the letter of the Ministry of Finance dated April 15, 2008 No. 03-04-06-01/86, resolutions of the FAS North-Western District dated February 21, 2008 No. A56-30516/2006, FAS North Caucasus district dated March 12, 2008 No. F08-478/08-265A, resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Ural District dated August 20, 2009 No. F09-5950/09-S2.
Looking ahead, let's say that tax officials are not alone in the desire to charge taxes and fees on the amount of the “holiday lunch”. Officials in the letter of the Ministry of Health and Social Development dated March 23, 2010 No. 647-19 propose to charge insurance premiums for payments in favor of employees, even if they are not specified in employment contracts.
However, in the absence of the ability to “personalize” the participation of each employee in the New Year’s corporate party, insurance premiums should not be charged (by analogy with personal income tax).