The essence and advantages of the commission agreement
A commission agreement is a fairly popular phenomenon in Russian business, and therefore widespread. The specificity of such a transaction is that the intermediary carries out all actions on his own behalf, but only within the framework strictly set by the seller of the goods and subject to certain restrictions.
Going beyond these limits is dangerous, since in this case the contract can be terminated unilaterally, and losses incurred by the owner of the inventory will be recovered from the seller.
All the subtleties of the legal relationship between the parties in such an agreement must be spelled out with particular care - in the event of inspections by supervisory authorities or any disputes and disagreements, this approach will allow us to understand the problem that has arisen, calculate sales and financial resources due to each of the parties.
The commission agreement has obvious advantages for participants:
- Compared to other types of legal relations, it allows the sale of goods belonging to one of the parties (the seller) without actually transferring them to the second party (the intermediary), i.e. formally, until the moment of transfer to the final buyer, inventory items remain the property of the seller;
- money for the transaction is also transferred directly to the seller’s account, bypassing the intermediary, who subsequently receives a certain remuneration for his services.
Receipt of goods from the consignor
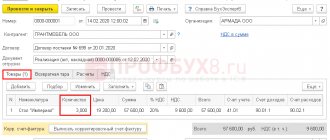
The transfer of goods from the consignor to the agent is subject to registration in the “Purchases” section, with the selected “Receipt” document. The item you need to select is “Goods, services, commission”.
Everything is simple here - we indicate the counterparty, the contract, the warehouse. Click on the “Add” button and select an item and start filling out the table.
You should always set the view to “Products on commission”.
The item can be transferred in advance to the “Products on commission” folder so that the type is set automatically.
We indicate the quantity, cost, but indicate VAT in this form - Without VAT. While filling out the accounting account, everything will be done automatically.
Due to the fact that the agent is not the owner of the goods, everything will be displayed on account 004 “Goods accepted for commission”.
What are “committent” and “commission agent”
In commission agreements, one of the parties is called the principal (this is the organization that owns the inventory items), the second is called the commission agent (an intermediary between the owner of the goods and the buyer).
The principal instructs the commission agent to conduct transactions for the purchase and sale of goods for a certain financial reward. At the same time, the percentage of remuneration may vary, depending on sales volume, timing of implementation and other factors.
The formats of commission transactions can also be different: one-time or permanent, in addition, it is permissible to carry them out using monetary units of other countries, bills of exchange, securities, etc.
Accounting entries of the principal
Below are examples of accounting entries:
| Operation | DEBIT | CREDIT |
| The commission agent sells the principal's property | ||
| The property was given to the commission agent for sale | 45 | 41 |
| Cash receipts from the sale of property are reflected | 62 | 90 |
| VAT amount charged | 90 | 68 |
| Write-off of the cost of property sold | 90 | 45 |
| A fee was paid to the intermediary | 44 | 76 Sat. “Settlements with commission agent” |
| The amount of VAT on the fee has been deducted | 19 | 76 Sat. “Settlements with commission agent” |
| Accounting for buyer's debt | 76 Sat. “Settlements with commission agent” | 62 |
| VAT deducted on the intermediary's fee | 68 | 19 |
| The account received income from the sale of property | 51 | 76 Sat. “Settlements with commission agent” |
| The commission agent buys property for the principal | ||
| Money was paid to the intermediary for the purchase of goods | 76 Sat. “Settlements with commission agent” | 51 |
| Receipt of goods from the counterparty | 10 | 60 |
| VAT calculation on purchased items | 19 | 60 |
| The amount of the intermediary's fee is added to the cost of the goods | 10 | 60 |
| VAT accrual on fees | 19 | 60 |
| Debt to counterparty taken into account | 60 | 76 Sat. “Settlements with commission agent” |
| Debt to intermediary taken into account | 60 | 76 Sat. “Settlements with commission agent” |
| VAT deducted | 68 | 19 |
| Remaining money from the transaction accepted | 51 | 76 Sat. “Settlements with commission agent” |
Example of accounting for a principal
ZAO Tenant sent property to OOO Posrednik for sale. According to the commission agreement, 350 thousand rubles will be earned for it (including VAT - 63 thousand rubles). The cost of the property is 175 thousand rubles. The commission agent's fee is 35 thousand rubles (including VAT – 6300 rubles).
Posrednik LLC completed the sale of the property. It participates in the calculations and has the right to withdraw the amount of its fee from the general money belonging to the Tenant CJSC. CJSC “Tenant” in its accounting policy approved work in the “shipment” mode for the purpose of calculating the amount of VAT. The accounting department of ZAO Tenant will make the appropriate entries.
Note: Sub-accounts were opened for the main accounts:
- 76-5 (Settlement with commission agent),
- 76-6 (Settlement with the principal),
- 76-7 (Settlement with the buyer).
| Operation | DEBIT | CREDIT | Amount (RUB) |
| The property was given to the warehouse of Posrednik LLC | 45 | 41 | 175000 |
| Revenues from sales are reflected | 62 | 90-1 | 350000 |
| Calculation of VAT amount on them | 90-3 | 68 | 63000 |
| Write-off of the actual cost of property sold | 90-2 | 45 | 175000 |
| The fee of Posrednik LLC is included in the sales costs | 44 | 76-5 | 28700 (35000 – 6300) |
| VAT credited on fees | 19 | 76-5 | 6300 |
| Accounting for commission agent's fees among payments for property sold | 76-5 | 62 | 35000 |
| VAT has been deducted for the service of LLC “Posrednik” | 68 | 19 | 6300 |
| Receipts for items sold minus intermediary fees are accepted. | 51 | 62 | (315000 – 35000) |
| Write-off of sales expenses | 90-2 | 44 | 28700 |
| Profit from the transaction | 90-9 | 99 | 83300 (350000 – 63000 – 175000 – 28700) |
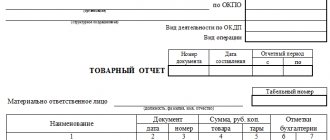
How to write a report
Today, there is no unified form for reporting to the committent, so representatives of enterprises and organizations have the right to write it in any form or according to a template developed within the company. The only condition: you need to ensure that the document complies with the norms of business documentation and office work standards, in addition, it must contain certain information.
In particular, the report must indicate:
- date and number of the document;
- names of partner enterprises (committent and commission agent);
- number and date of the commission agreement within the framework of which this document is formed.
Next, the report should contain the main part, designed in the form of a table, where information about the goods sold is entered in numbers:
- Product Name;
- volume;
- price;
- benefit received;
- information about the documents accompanying each transaction;
- information about suppliers;
- the overall result of the commission agent's activities.
The table may be supplemented with some other columns (depending on the conditions specified in the commission agreement).
The next part of the document somewhat explains the above table. The financial side of the matter is described in detail here:
- total cost of goods purchased;
- amount of remuneration and additional benefit;
- other aspects specified in the contract.
Finally, it is indicated that the committent may object to the information provided within a certain period of time.
Accounting with the principal when selling goods through a commission agent in 1C
Let's look at the reflection of households. transactions with the principal under a commission agreement in 1C 8.3 Accounting 3.0. Before you start using the program, you need to configure 1C 8.3 to work with transactions under a commission agreement:
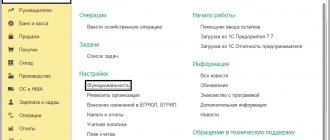
- Open the “Main” tab, select “Functionality” in the “Settings” column;
- Open the “Trade” tab and check the box next to:
- “Sale of goods and services of principals (principals)”,
- “Sale of goods and services through commission agents (agents)”,
- “Purchase of goods and services for principals (principals)”,
- “Purchase of goods and services through commission agents (agents).” Ready.
In all calculations in the documents, the fee for services withheld by the intermediary will be taken into account; this can be verified by opening the balance sheet for account 76-09.
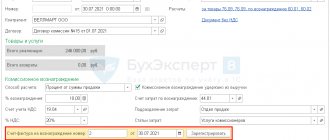
Operation: transfer of property to an intermediary
- Create a new document: select “Sales”, “goods, services, commission”;
- For an intermediary, in the “Type of agreement” column, select “With a commission agent (agent) for sale”, in the “Counterparty” line, enter the name of his company;
- Fill in the contract information requested by the program;
- The document will make the necessary entries.
Operation: creating a commission agent's report on a transaction during which the principal's property was sold (click to expand)
- Click “Create based on”, select “Implementation document”.
- Open the “Main” tab, indicate the accounts of the calculations performed by clicking on the hyperlink. Select a calculation method from the list. If the intermediary deducts the fee from the principal’s total amount of money, check the box next to the inscription “Commission deducted from the proceeds”;
- Open the “Sales” tab. In the “Buyer” column, indicate the buyer who received the principal’s property through an intermediary. If an invoice was issued to the buyer, check the “Invoice” column, and it will be issued by the program.
- The invoice is reissued by the intermediary, so that in the “Organization” column you need to indicate the principal, and in the “Counterparty” - the buyer of the principal’s property. It will be entered in the Sales Book. Read also the article: → “Invoice: sample filling, form.”
- Open the “Cash” tab, write down data on the revenue resulting from the purchaser’s payment for the goods. The postings will be generated by the program. The invoice is subject to registration in the Sales Book.
Operation: registration of an invoice for the commission agent's fee
- Click on the “Create based on” list, select “Commissioner (agent) sales report”
- The program will fill in the data itself; and the document will carry out the postings.
Operation: acceptance of proceeds from the commission agent for sold property
- Click on “Create based on”, select “Report of the commission agent (agent) on sales.” The program enters the information itself.
- Post the document “Receipt to account”, he will make the postings himself.
How to submit a report
You can prepare the report either in handwritten form or in printed form (the second option, of course, is more convenient), on letterhead or on a regular A4 sheet.
The main condition is that it contains the original signature of the commission agent (after receiving his copy, the committent also endorses the document).
It is not necessary to certify report forms using stamps, because since 2016, commercial companies (enterprises and organizations) can use various types of stamps in their activities only when this norm is enshrined in their local regulations.
The report is always generated in two copies , one of which remains with the commission agent, the second is transferred to the principal.
VAT on advances for commission agent services
Upon completion of the intermediary’s operations for the sale of the principal’s property, they are provided with a report and an invoice to receive a well-deserved fee, which will be registered with the principal in Part 2 of the register of records of received and issued invoices and in the purchase book.
VAT on the amount of fees for intermediary services and on the amount of compensation for the commission agent's expenses can be taken into account when calculating the tax base only after accounting for these costs, and only if invoices have been saved.
“Input” VAT on the fee of the commission agent for the sale of the tenant’s property will be taken as a deduction when calculating the taxable base of the principal.
When offsetting mutual claims, the VAT amount is paid to the commission agent who sold the principal's goods in a separate payment order, but this does not need to be done in the case where the intermediary independently deducts the amount of his fee for services from the total amount of the employer's funds.
When selling goods of the consignor:
- Accounting for the amount of VAT on the fee of the intermediary company: D 19 K 76 sub. “Settlements with the commission agent.”
- VAT deduction on the intermediary's fee: D 68 K 19.
When purchasing goods for the consignor:
- Accounting for VAT on the commission agent's fee: D 19 K 60.
- VAT deduction for payment of intermediary services: D 68 K 19.
Optimal deadline for submitting a report
As stated above, the commission agent submits a notice of sale to the principal within three days after the end of the period. Therefore, experts recommend that when drawing up a commission agreement, set the same deadline for submitting the commission agent’s report.
By the way, such frequency can also be beneficial for the commission agent himself, if, within the framework of the commission agreement, he is engaged in the acquisition of goods for the principal. In accordance with Article 996 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the commission agent can deduct “input” VAT on these expenses, since he is actually the buyer of the goods. However, in order to reduce the calculated VAT, this deduction must be reflected in the tax return. Accordingly, in order to reflect the amount of the deduction in the declaration for the current period, the commission agent's report must relate to this period.
Of course, for the commission agent the above remark is not so critical, because he will be able to claim VAT for deduction later on the basis of clause 1.1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. But if it is necessary to take advantage of VAT deduction without transfer to subsequent periods, the commission agent should take into account that a report on the sale of goods must be drawn up immediately.
Implementation and presentation of the report in different periods
By agreement between countries, the commission agent can submit a report on each fact of implementation, and also do this with a certain frequency or after completing the entire order.
However, when choosing the frequency of submission of the report, it is worth considering that on its basis the committent calculates VAT. And there is one nuance here - the base for this tax is determined at the time of sale of the goods. This is stated in paragraph 16 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated May 30, 2014 No. 33. Thus, the principal must charge VAT in the tax period when the commission agent sold his goods.
In accordance with Article 316 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, proceeds from sales must be determined by the principal on the basis of a notice of sale received from the commission agent. The commission agent is given three days to notify the principal of the sale of the goods.
However, in a situation where the contract provides for the submission of a report, say, after the sale of the entire volume of goods transferred to the commission, a discrepancy may arise: the sale was recorded in one period, and the report was received in another.
Since the principal has already reported VAT for the period to which the sale of his goods relates in accordance with the received report, he will have to recalculate the amount of tax and submit an updated declaration. Indeed, based on paragraph 1 of Article 54 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, if in the current period errors were discovered in determining the tax base for previous periods, they should be corrected. Moreover, it is necessary to adjust the tax accounting registers, the tax base and the amount of VAT for the period in which the errors were made.
Is it possible, instead of filing an updated declaration, to include income from goods previously sold by the commission agent in the VAT base for the current period? No, you shouldn’t do this, because the risk of sanctions from the Federal Tax Service is too great. During the inspection, experts will consider that in the period when the goods were actually sold by the commission agent, the principal did not reflect this sale and underestimated the amount of VAT. As a result, additional taxes, fines and penalties will follow.